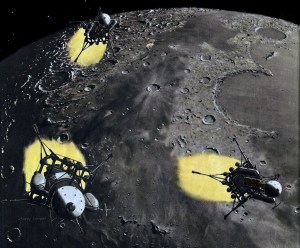
The first trip to our moon will be without landing, in a ship designed to travel in space only, taking off near the Space Station and returning to it. Here the round-the-moon ship is some 240,000 miles from earth, 50 miles above the lunar surface. The large crater is Aristillus (diameter 35 miles); the other crater is Autolycus; the distant mountains are the lunar Apennines.
Man will Conquer Space Soon
Collier’s, March 22, 1953
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: Mike Acs