Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 18,1952
Image credit: Colliers
Image source: AIAA Houston

More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

The first trip to our moon will be without landing, in a ship designed to travel in space only, taking off near the Space Station and returning to it. Here the round-the-moon ship is some 240,000 miles from earth, 50 miles above the lunar surface. The large crater is Aristillus (diameter 35 miles); the other crater is Autolycus; the distant mountains are the lunar Apennines.
Man will Conquer Space Soon
Collier’s, March 22, 1953
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: Mike Acs

Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: NASA Images



How Man will Meet Emergency in Space Travel
Collier’s, March 14, 1953
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

Before space-going rocket tries out its power, it will undergo tow tests behind jet bomber. Crew will board it, try emergency procedures–including bail-out, shown above.
How Man will Meet Emergency in Space Travel
Collier’s, March 14, 1953
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston


More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston


Is there Life on Mars?
Collier’s, April 30, 1954
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston


Is there Life on Mars?
Collier’s, April 30, 1954
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

After 15 month exploration, the Mars expedition prepares for return flight to earth. Two landing planes are set on tails, with wings and landing gear removed. They will rocket back to the 600-mile orbit on first leg of journey.
Is there Life on Mars?
Collier’s, April 30, 1954
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

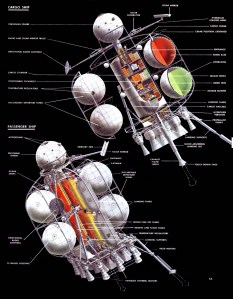
The unloading on the moon. Twenty-four hours after landing, supplies have been stowed in caterpillar tractors. Hold of cargo ship (r.) is being lowered to ground in sections, to be used as prefabricated headquarters, Earth is at center; halo effect is caused by sun, hidden behind sphere of rocket ship at left. Diagonal streak in sky, the zodiacal light, is caused by sun’s ray reflecting from cosmic dust. The red star at left is Mars.
More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

Causing moonquakes. Rockets with explosive war heads are fired off and scientists check the vibrations waves caused by distant blast, to determine interior composition of the moon. Seismograph in foreground is push-button controlled and surveying instrument to it’s left has cupped headpiece, to accommodate hooks and helmets of expedition members.
More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston