
Image Credit: NASA
Image source: Mike Acs

Image Credit: NASA
Image source: Mike Acs

S75-25941 (April 1975) — An Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) symbolic painting by artist Bert Winthrop of Rockwell International Space Division, Downey, California. The artwork is composed of the ASTP mission insignia, the docked Apollo-Soyuz spacecraft, and portraits of the five ASTP prime crewmen, all superimposed against Earth’s sphere in the center of the picture. The launches of both the American ASTP space vehicle (on left) and the Soviet ASTP space vehicle are depicted in the lower right corner. The five crewmen are, clockwise from the ASTP emblem, astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American crew; astronaut Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot of the American crew; astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American crew; cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, engineer on the Soviet crew; and cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet crew. The joint U.S.-USSR ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for July 1975.
Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images
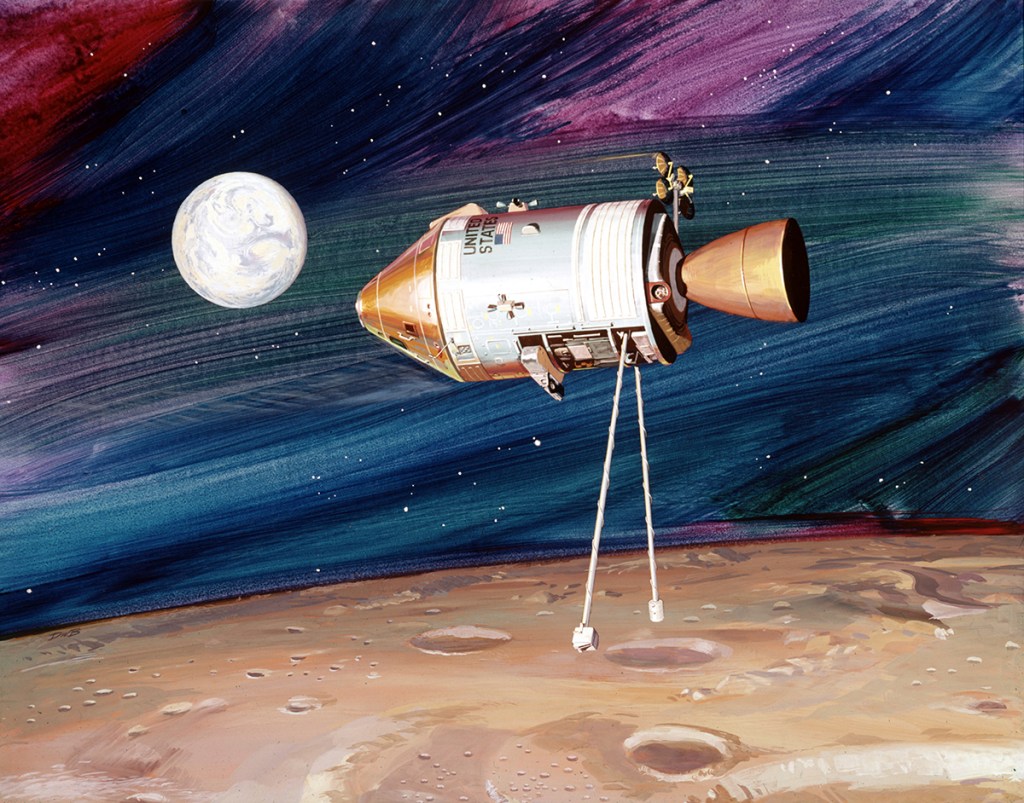
Image credit: NASA
Image source: Drew Granston
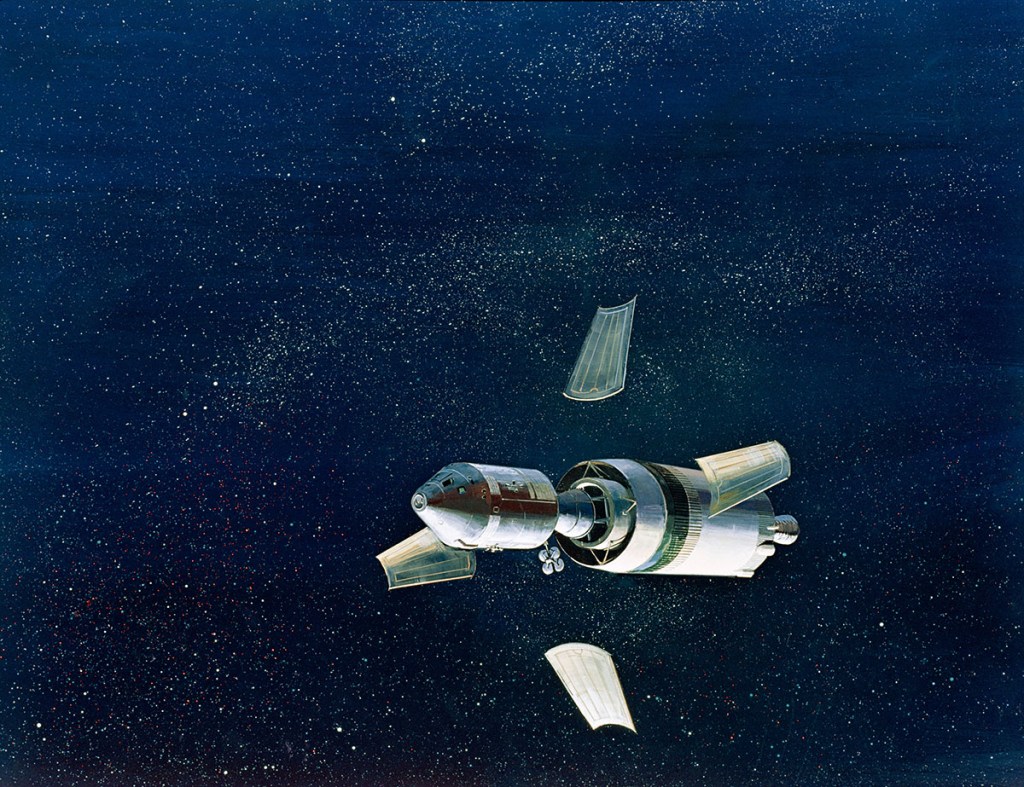
Image credit: NASA
Image source: NASA Johnson





Top Left: Flight Crew Preparation
Top Right: Orbital Insertion
Middle Left: 103 N. Mile Orbit
Middle Right: Separation
Bottom Left: Docking
Bottom Right: Docked SPS Burn




Top Left: Landmark Tracking
Top Right: Pitch Maneuver
Bottom Left: Yaw-Roll Maneuver
Bottom Right: High Apogee Orbits

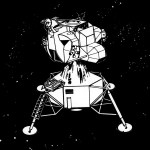
Left: Crew Transfer
Right: LM System Evaluation


Top Left: Camera
Top Right: Day-Night EVA
Bottom Left: Golden Slippers
Bottom Right: TV – Texas, Florida


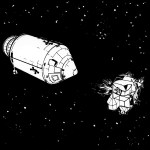
Top Left: Vehicles Undocked
Top Right: Burns For Rendezvous
Middle Left: Maximum Separation
Middle Right: APS Burn
Bottom Left: Formation Flying And Docking
Bottom Right: LM Jettison Ascent Burn


Left: Service Propulsion Burns
Right: Landmark Sightings, Photograph Special Tests



Top Left: CM/SM Separation
Top Right: Re-Entry
Image credit: NASA JSC
Images: NASA Images
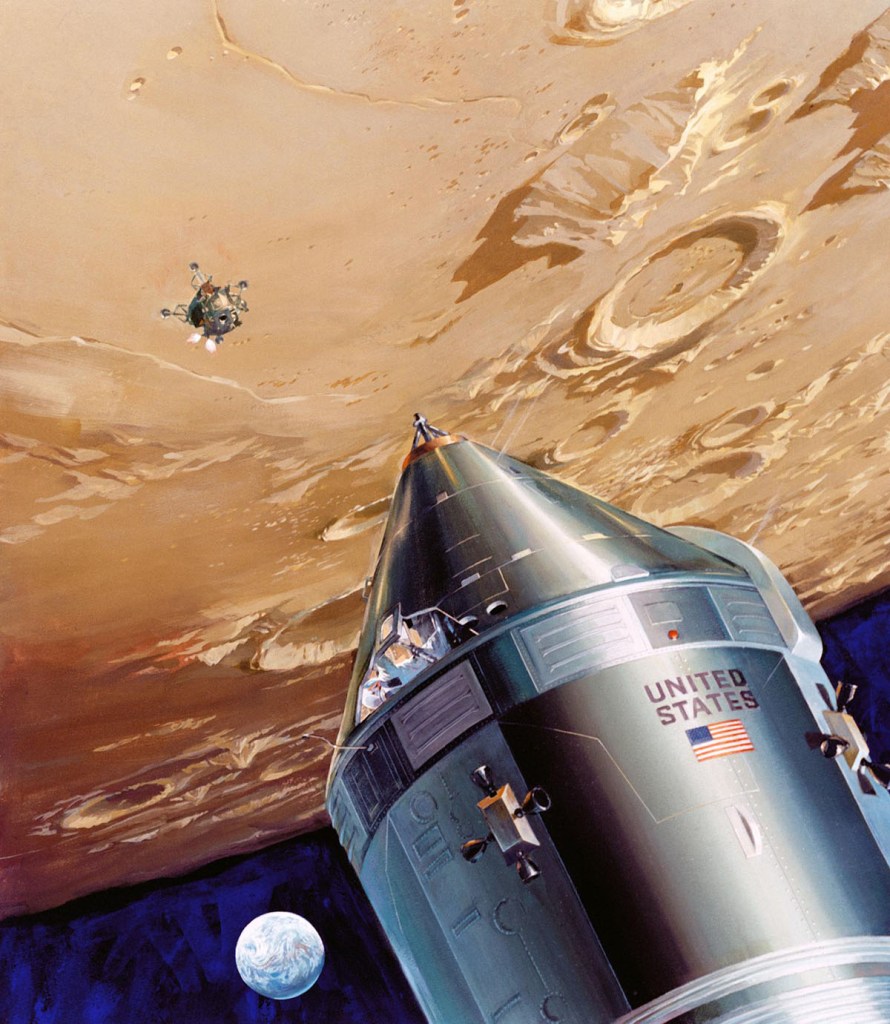

Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images

S71-39481 (July 1971) — An artist’s concept showing TRW’s small lunar subsatellite being ejected into lunar orbit from the SIM bay of the Apollo 15 Service Module. The 80-pound satellite will remain in orbit a year or more, carrying scientific experiments to study space in the vicinity of the moon. The satellite carries three experiments: S-Band Transponder; Particle Shadows/Boundary Layer Experiment; and Subsatellite Magnetometer Experiment. The subsatellite is housed in a container resembling a rural mailbox, and when deployed is spring-ejected out-of-plane at 4 fps with a spin rate of 140 rpm. After the satellite booms are deployed, the spin rate is stabilized at about 12 rpm. The subsatellite is 31 inches long and has a 14 inch hexagonal diameter. The exact weight is 78.5 pounds. The folded booms deploy to a length of five feet. Subsatellite electrical power is supplied by a solar cell array outputting 25 watts for dayside operation and a rechargeable silver-cadmium battery for nightside passes.
Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images
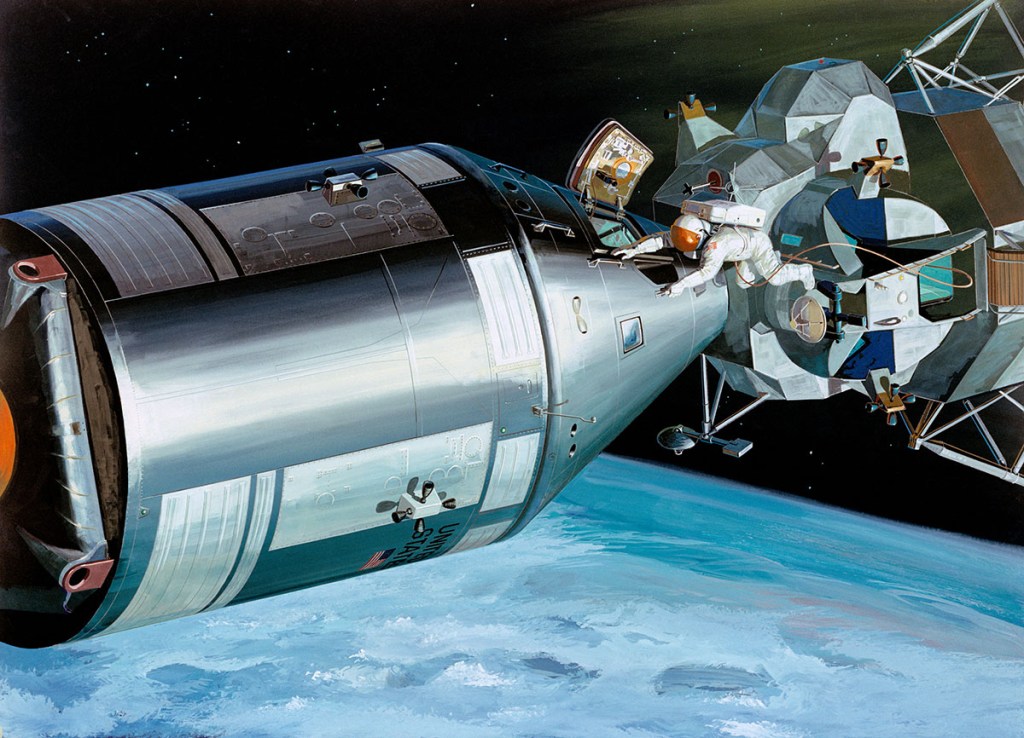

Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images

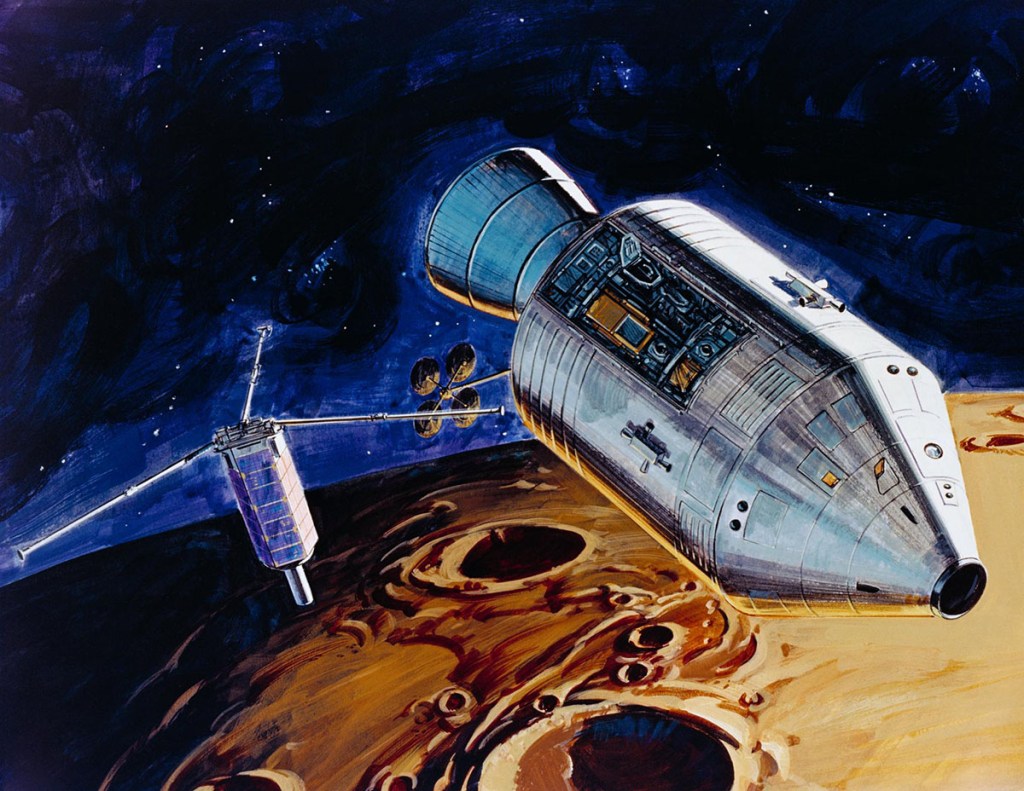
S72-53472 (November 1972) — An artist’s concept illustrating how radar beams of the Apollo 17 lunar sounder experiment will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon’s surface from the orbiting spacecraft. The Lunar Sounder will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) was developed by North American Rockwell’s (NR) Space Division for NASA’s Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images
Image credit: North American Rockwell
Image source: Numbers Station