Mar 17 1969
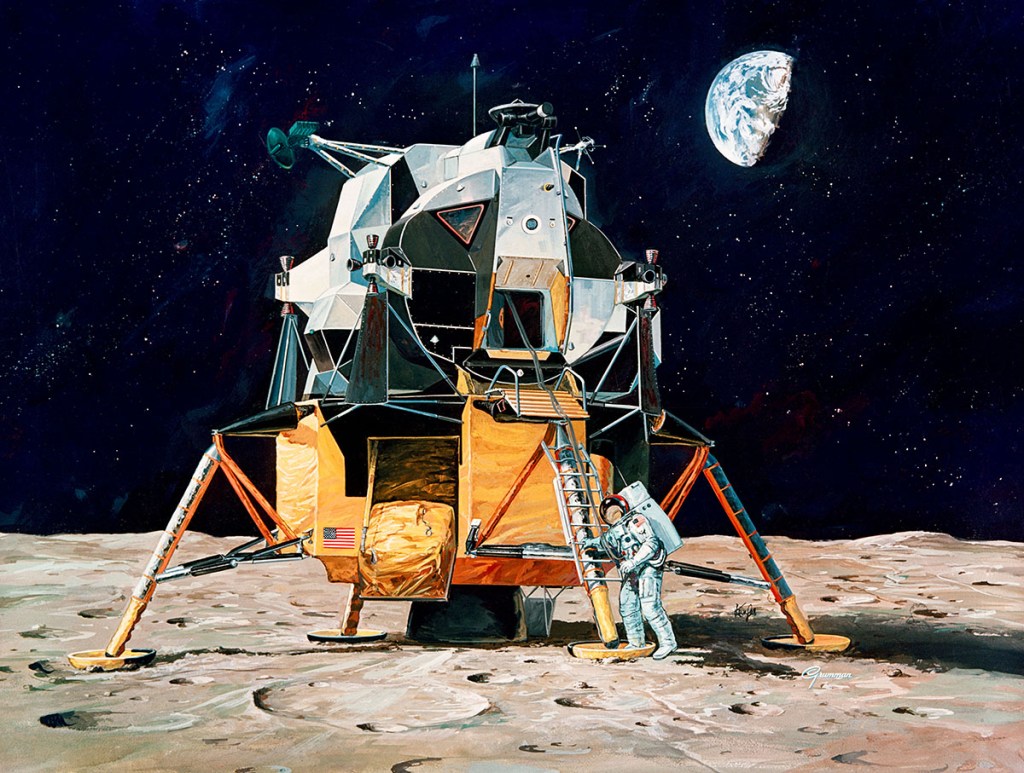
When America’s first two-man team lands on the moon, one of their first tasks will be to obtain a sample of lunar material as quickly as possible in event they have to make an emergency takeoff. If things go well, they will spend 25 hours on the surface, gathering up to 80 pounds of rocks, dust and other material to be put into vacuum-sealed containers. This sketch shows one astronaut gathering samples from a crater while his companion watches from the lunar module. Later, the two will roam up to 300 feet from the craft, working on a “buddy” system, to plant several measuring devices on the surface which will radio information to earth.
MAR 17 1969 COPYRIGHT, SEATTLE TIMES CO.
Image credit: NASA
Image source: Numbers Station