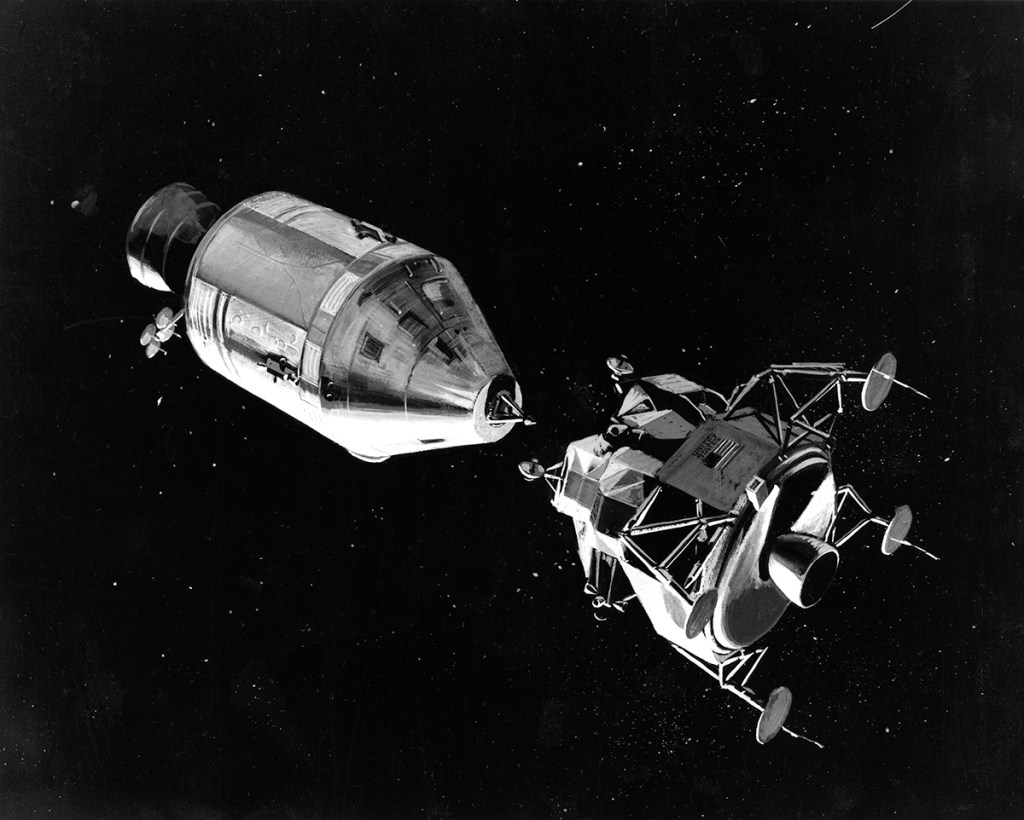
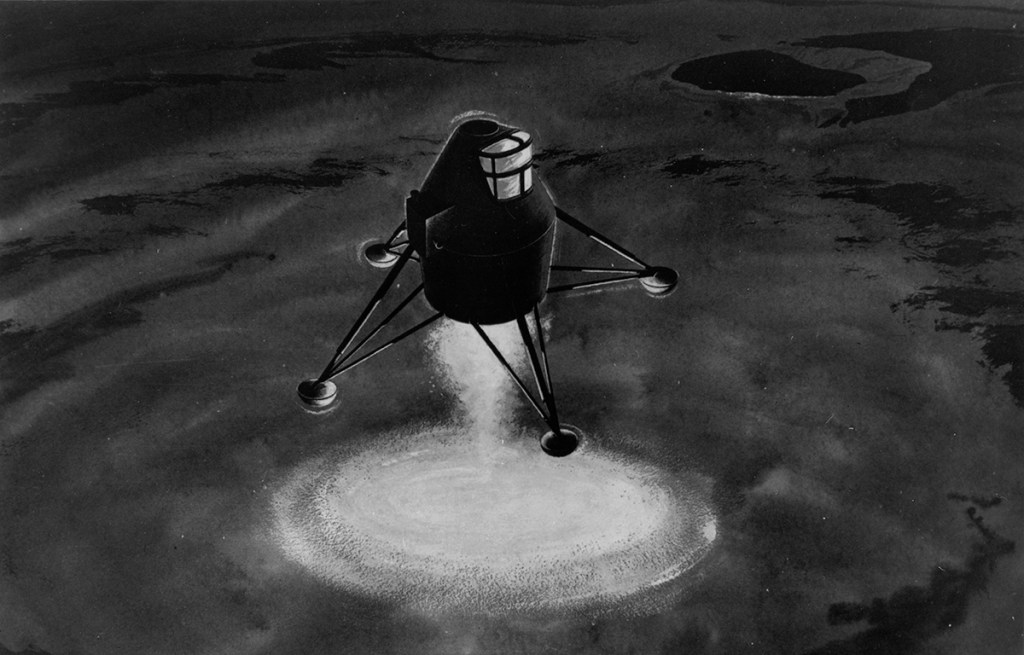
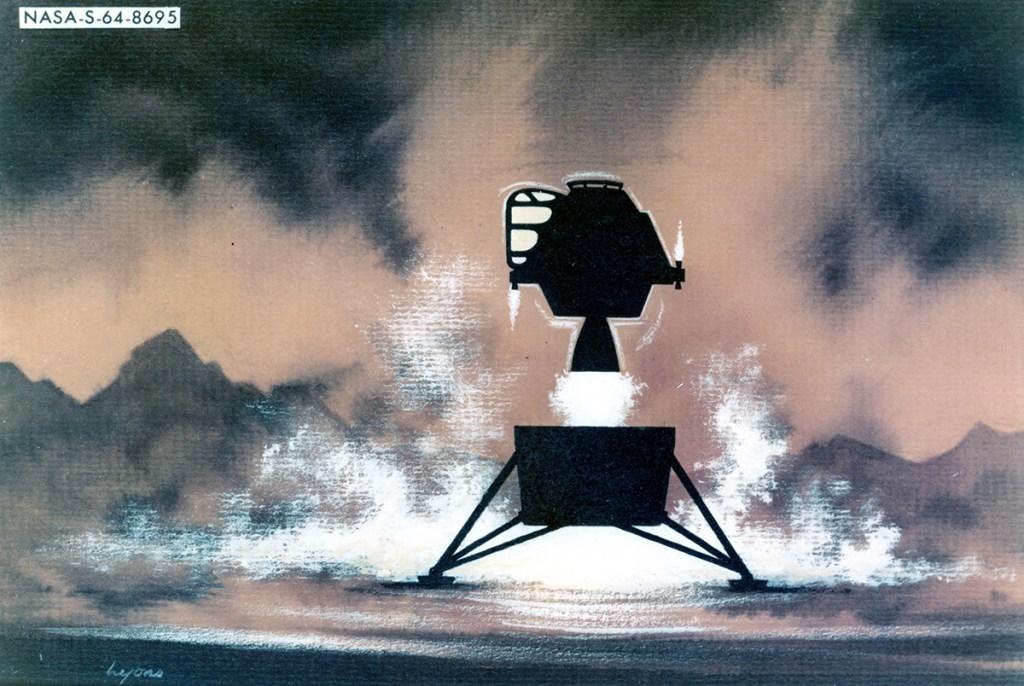
S69-39011 (July 1969) — TRW Incorporated’s artist concept depicting the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) descending to the surface of the moon. Inside the LM will be astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. TRW’s LM descent engine will brake Apollo 11’s descent to the lunar surface. The throttle-able rocket engine will be fired continuously the last 10 miles of the journey to the moon, slowing the LM to a speed of two miles per hour at touchdown. TRW Incorporated designed and built the unique engine at Redondo Beach, California under subcontract to the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, Bethpage, New York, the LM prime contractor.
Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images