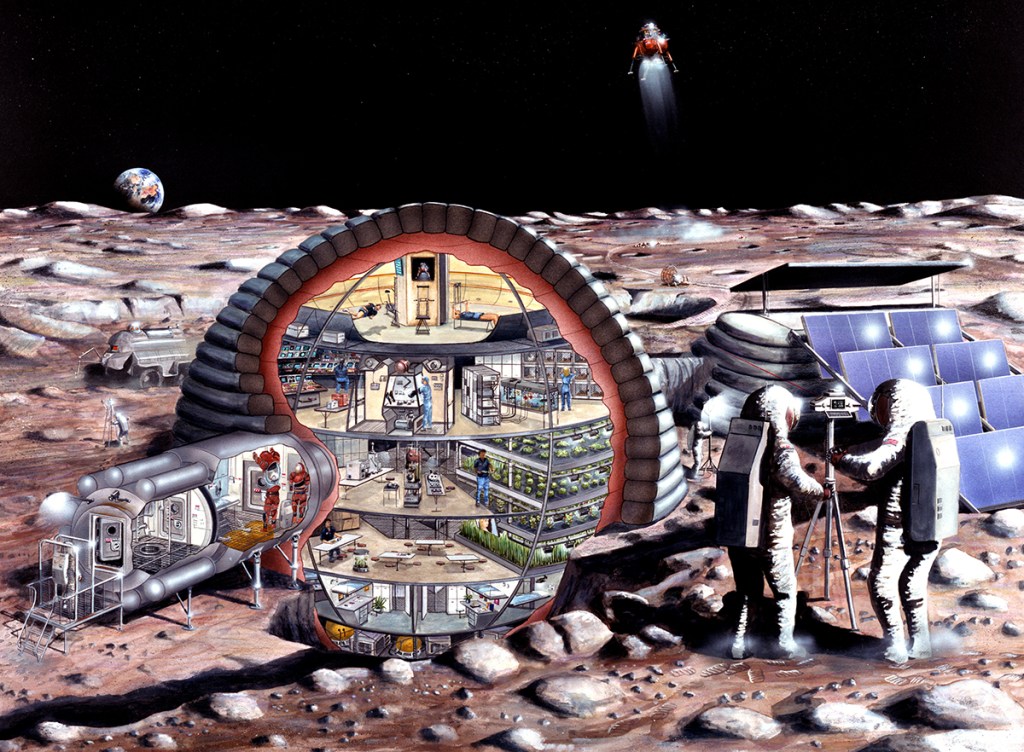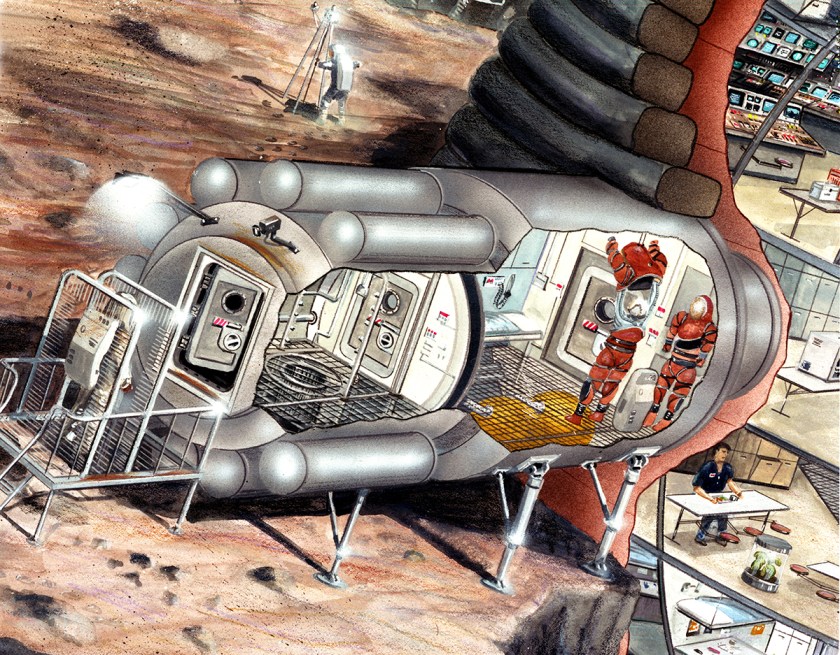
S89-20088 (July 1989) — With a number of studies ongoing for possible lunar explorations, many concepts for living and working on Earth’s natural satellite have been examined. This art concept reflects the evaluation and study at JSC by the Man Systems Division and Johnson Engineering personnel. A major concern of planners is the fine dust which covers the lunar surface and collects easily on astronauts garments, as evidenced by six crews of Apollo moon explorers. This special annex to the 16-meter diameter inflatable habitat (depicted in S89-20084/85) provides possible solutions to the dust problems, according to teams studying possible lunar expeditions. As much dust as possible must be removed, they say, before re-entering the habitat. The astronauts might pass through wickets (far left) which remove much of the dust. A performated metal “porch” would allow dust to fall through. Once inside the dust lock (center) the astronauts would remove their white coveralls. This outer garment would provide an extra layer of dust control and protection for the precision moving joints of the space suit from gritty dust. An air shower could remove remaining dust with strong jets of air. An astronaut at right, after having removed as much dust as possible, would be able then to move into the airlock to doff his suit. The airlock could accommodate up to four astronauts at one time. Suits could be stored there when not in use.
Image credit: NASA
Image source: NASA Johnson