Image credit: NASA
Image source: NASA NTRS


Image credit: NASA
Image source: NASA NTRS
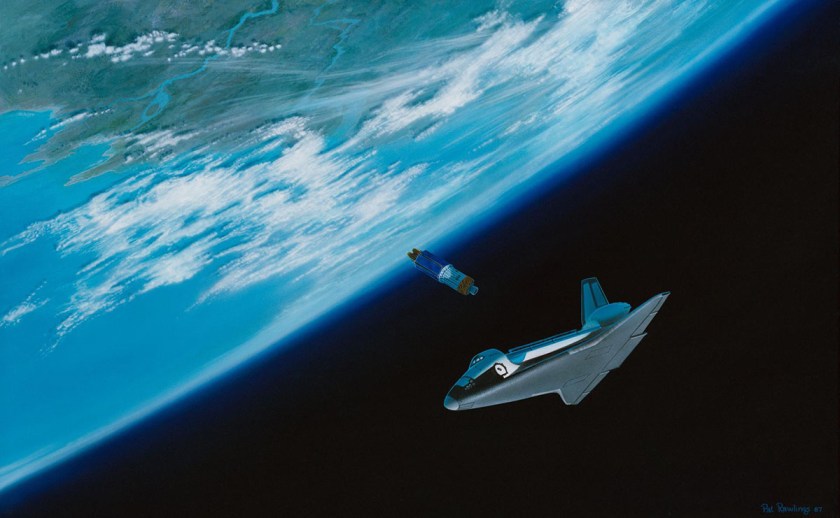

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, artwork depicts tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) deployment. OV-103 orbits above Earth in bottom-to-sun attitude, moments after TDRS-C’s release into space. TDRS-C is seen just below open payload bay (PLB). Artwork was done by Pat Rawlings of Eagle Engineering.
Image credit: NASA JSC
Image source: NASA Images
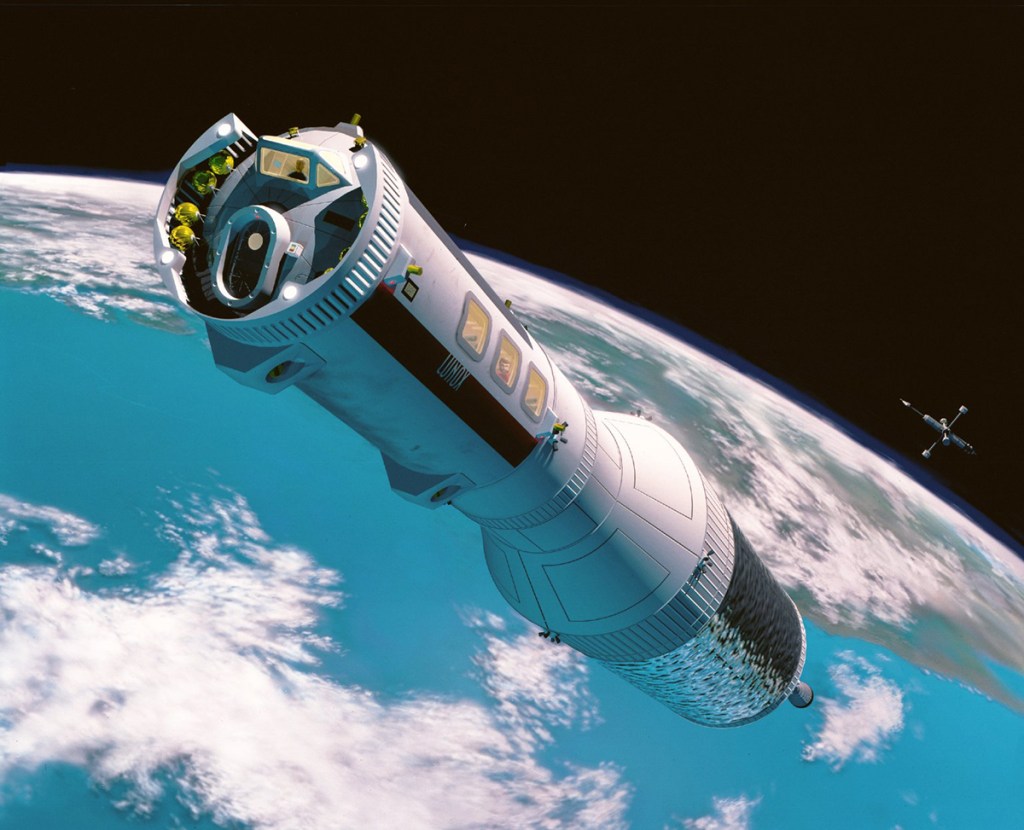

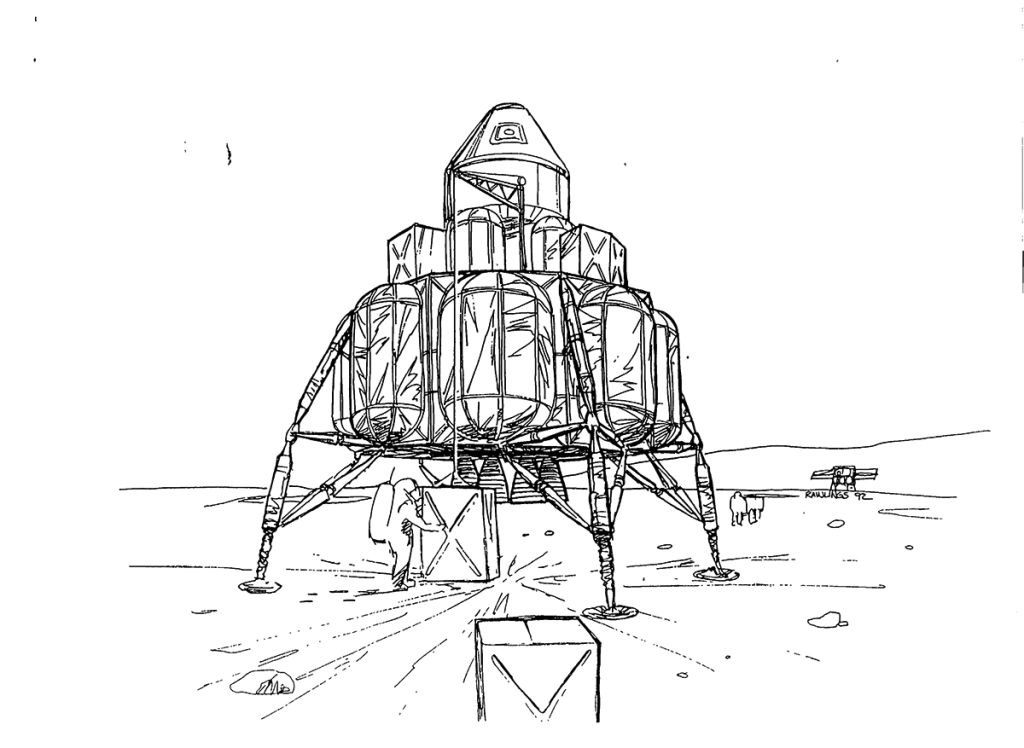
S99-04186 (1996) — Routine 24-hour flights to the Moon could employ detachable crew modules atop nuclear thermal transfer vehicles. By transferring the module from one propulsion element to the next, the passengers could complete their trip to the lunar surface without ever leaving the module. This image produced for NASA by Pat Rawlings and Bill Gleason, (SAIC). Technical concepts for NASA’s Exploration Office, Johnson Space Center (JSC).
Image credit: NASA LRC
Image source: Internet Archive

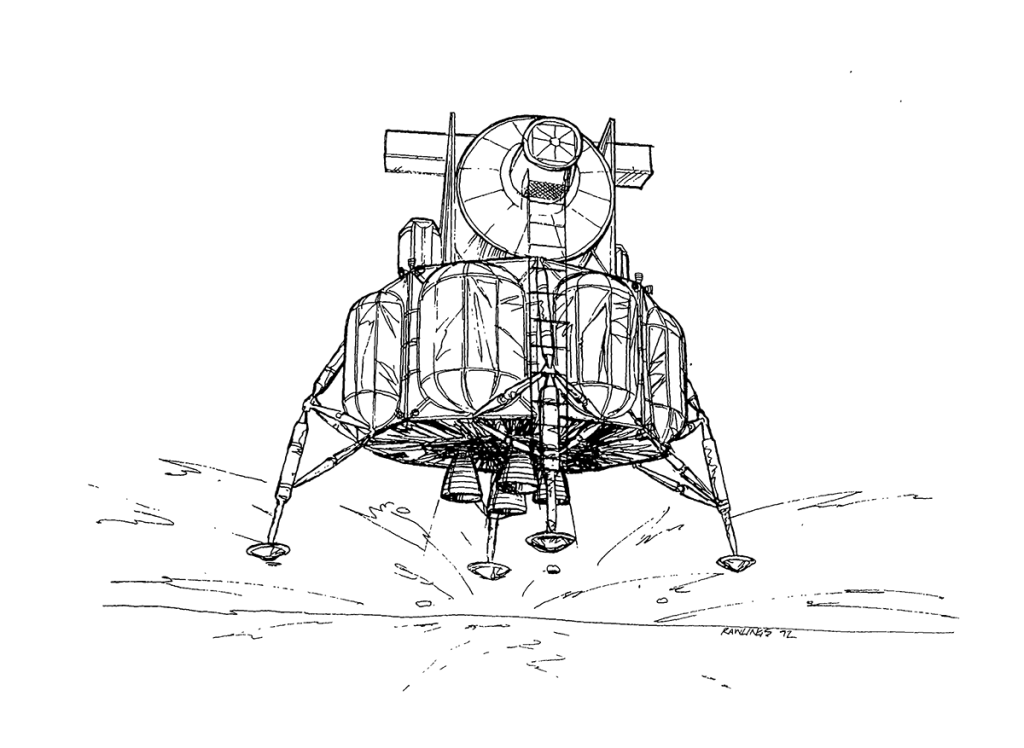
S83-28321 (14 March 1983) — In this artist’s concept of future lunar operations, a lunar ferry is about to burn out of lunar orbit for the trip back to facilities in low Earth orbit. The ferry vehicle carries tank modules filled with liquid oxygen, which has been produced from mining operations on the surface of the Moon. One possibility for such operations would be to have manned facilities in low lunar orbit, such as illustrated here. At the upper right side of the photo is a small orbiting manned station. At the lower right side of the photo is a liquid oxygen propellant dump, to which a lunar landing vehicle carrying liquid oxygen is about to dock. The lunar ferry vehicle itself is representative of one type of aerobraking system. The balloon-like torus around the center of the ferry-craft would inflate to several times its illustrated size and, once the vehicle has swooped down close to the Earth’s outer atmosphere on the return journey, would use atmospheric drag to slow the craft and place itself in low Earth orbit. The liquid oxygen would then be used in operations there for fueling various vehicles, including an orbital transfer vehicle for trips to geosynchronous Earth orbit. This concept is part of a study done for the Johnson Space Center by Eagle Engineering of Houston. The artist was Pat Rawlings.
Image credit: Eagle Engineering
Image source: Internet Archive