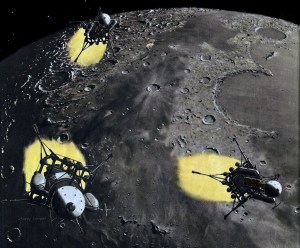
The unloading on the moon. Twenty-four hours after landing, supplies have been stowed in caterpillar tractors. Hold of cargo ship (r.) is being lowered to ground in sections, to be used as prefabricated headquarters, Earth is at center; halo effect is caused by sun, hidden behind sphere of rocket ship at left. Diagonal streak in sky, the zodiacal light, is caused by sun’s ray reflecting from cosmic dust. The red star at left is Mars.
More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston