Selected Plates From:

(NASA-CR-141856)
FUTURE SPACE TRANSPORTATION STUDIES ANALYSIS STUDY, PHASE 1 TECHNICAL REPORT
PROGRAM OPTIONS
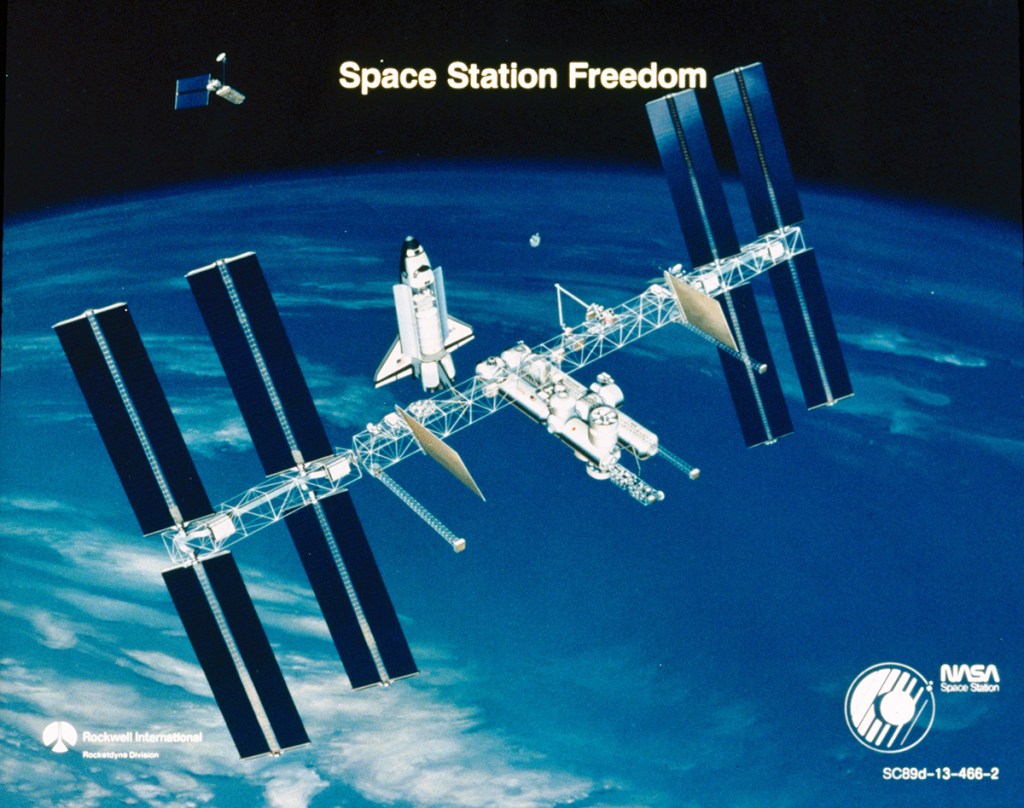
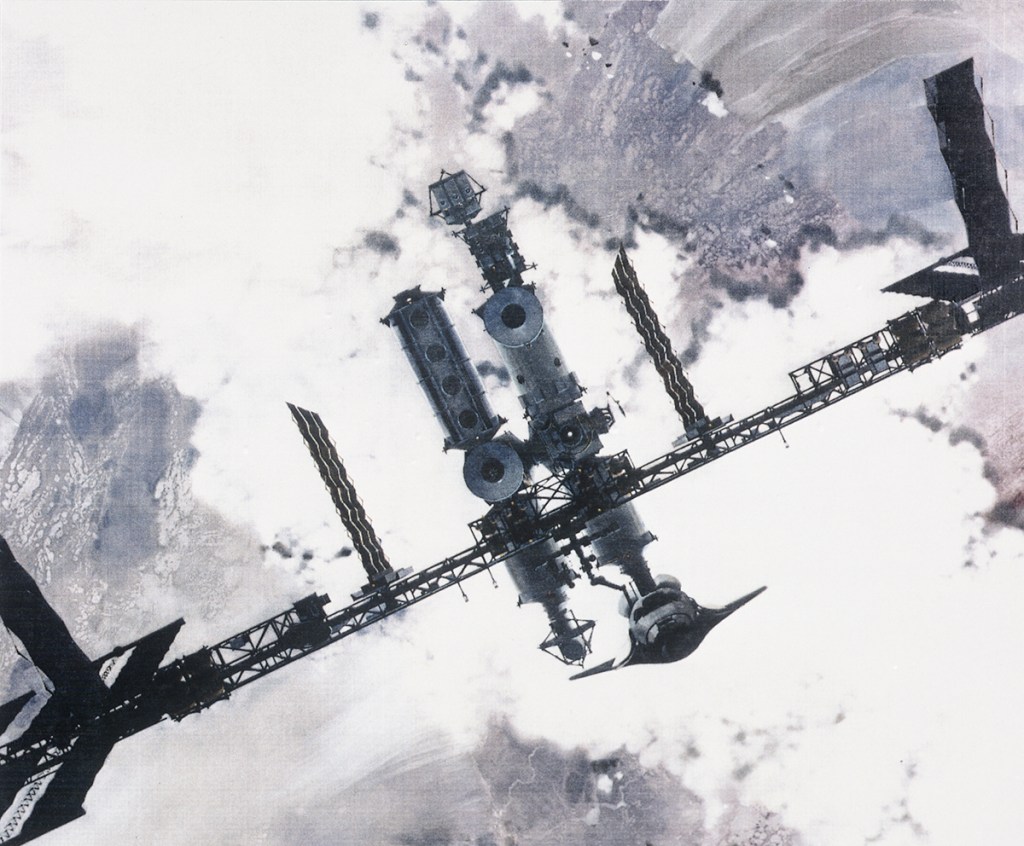
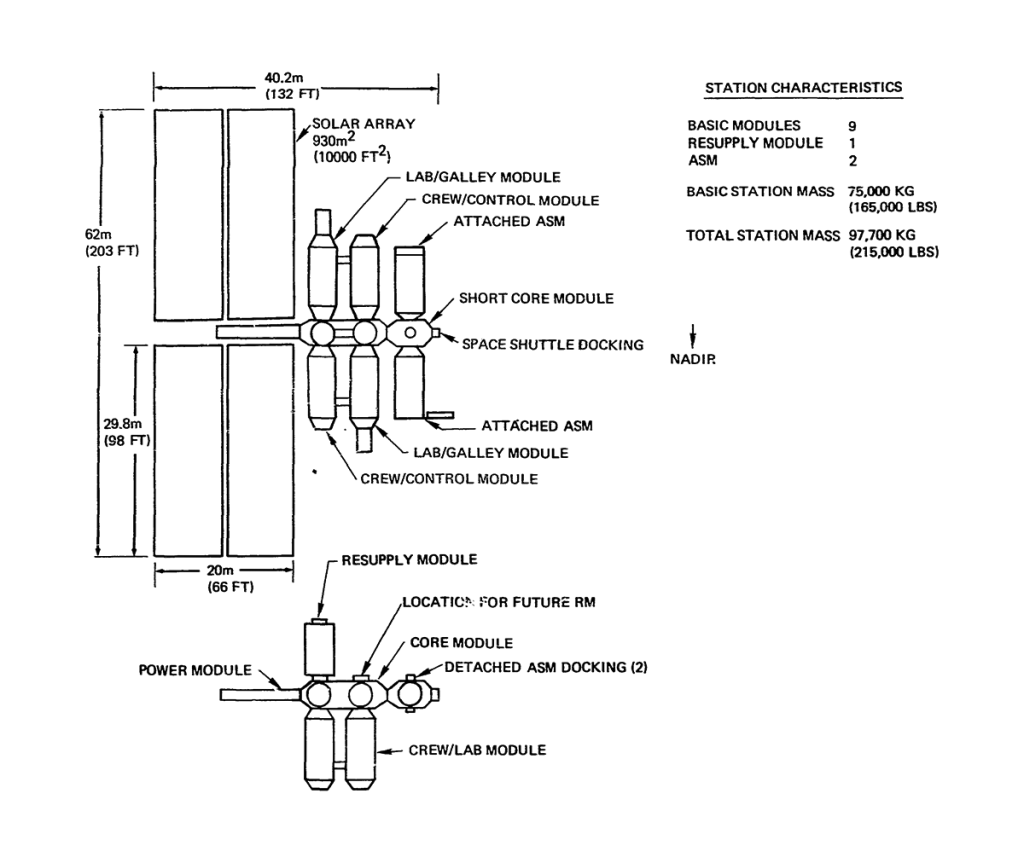
- Low Earth Orbit Space Stations
- 12-man modular or unitary station
- 60-man space base
- Geosynchronous Operations
- 12-man modular or unitary station
- Satellite maintenance sortie
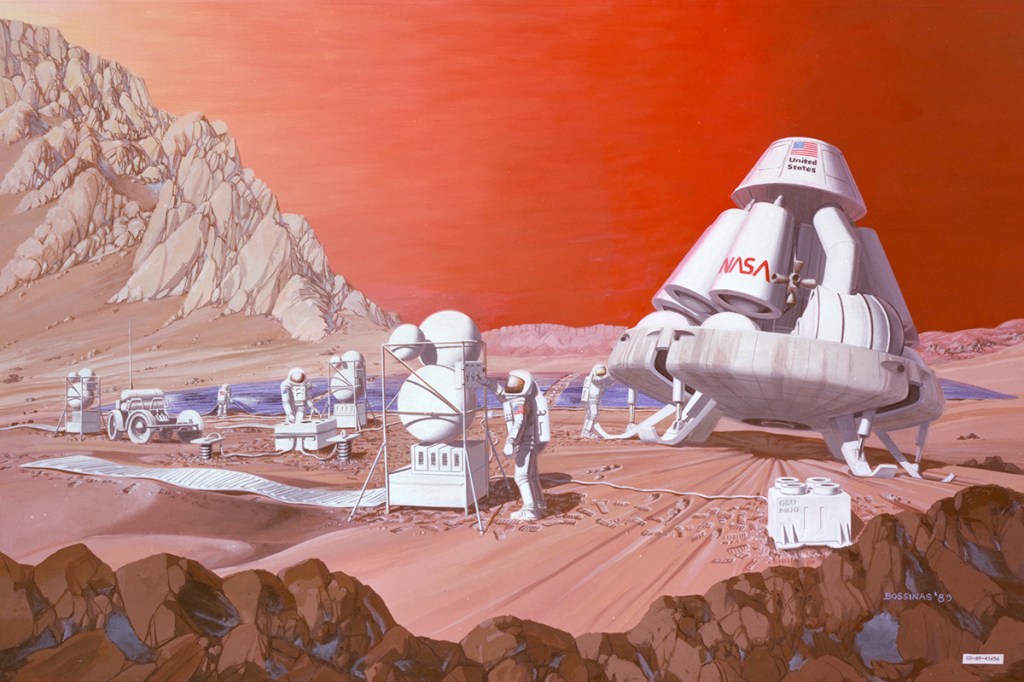
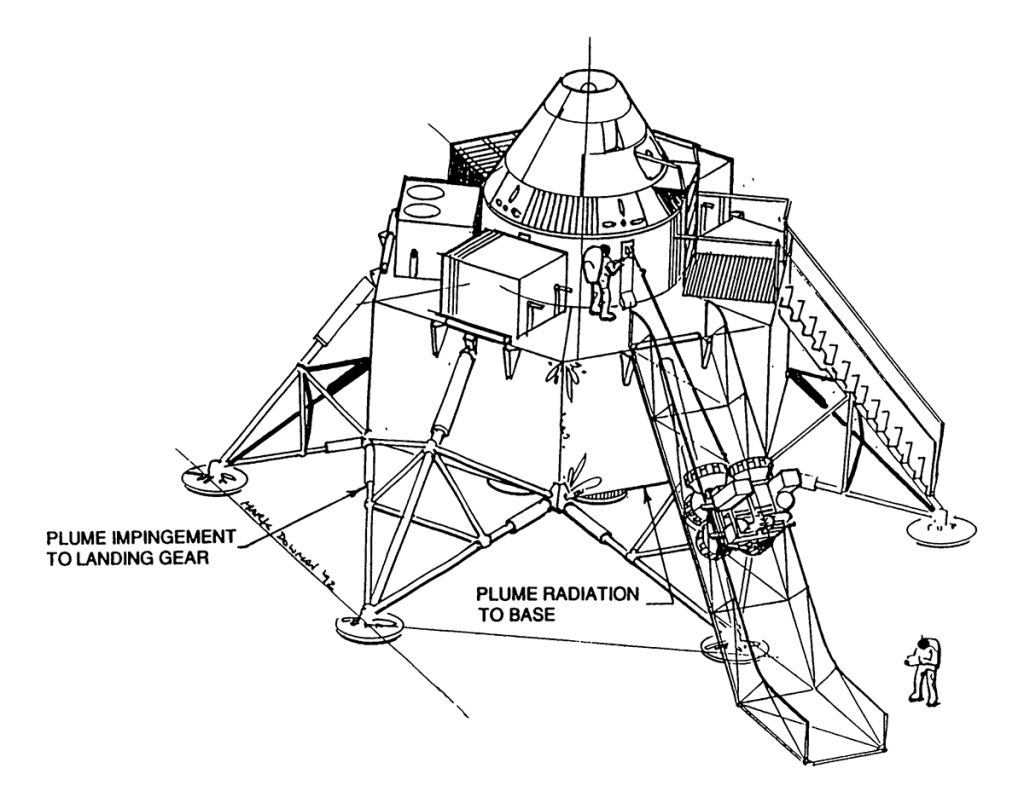
- Independent Lunar Surface Sorties
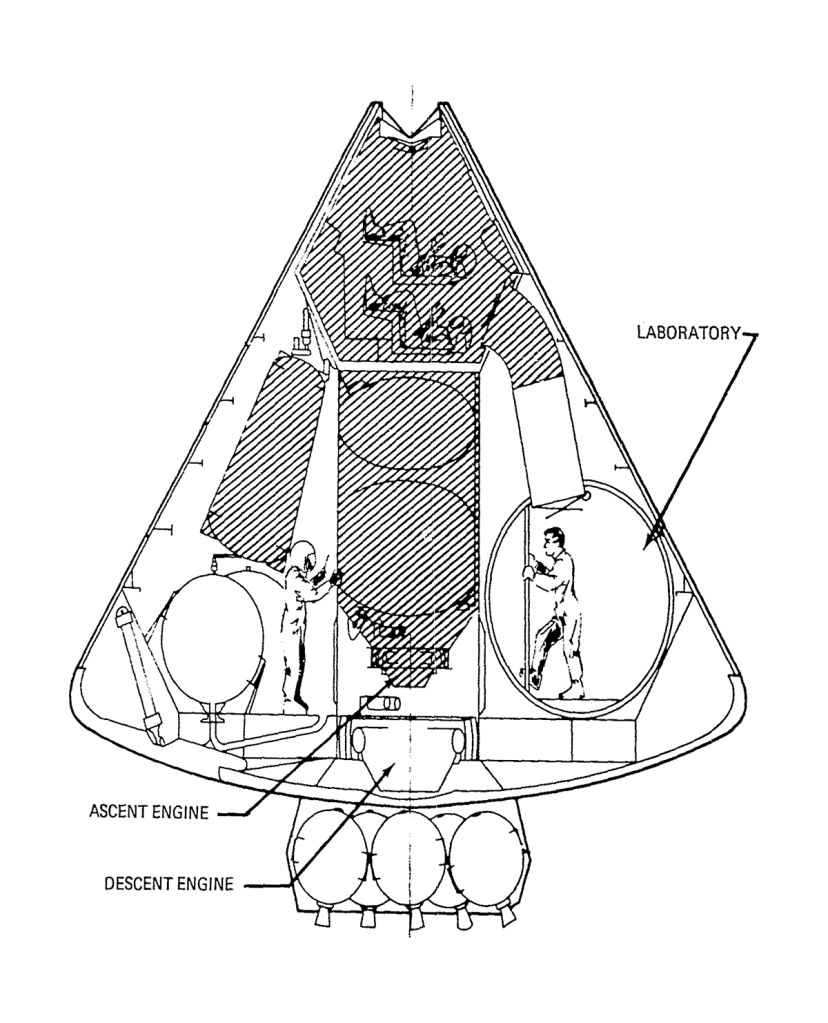
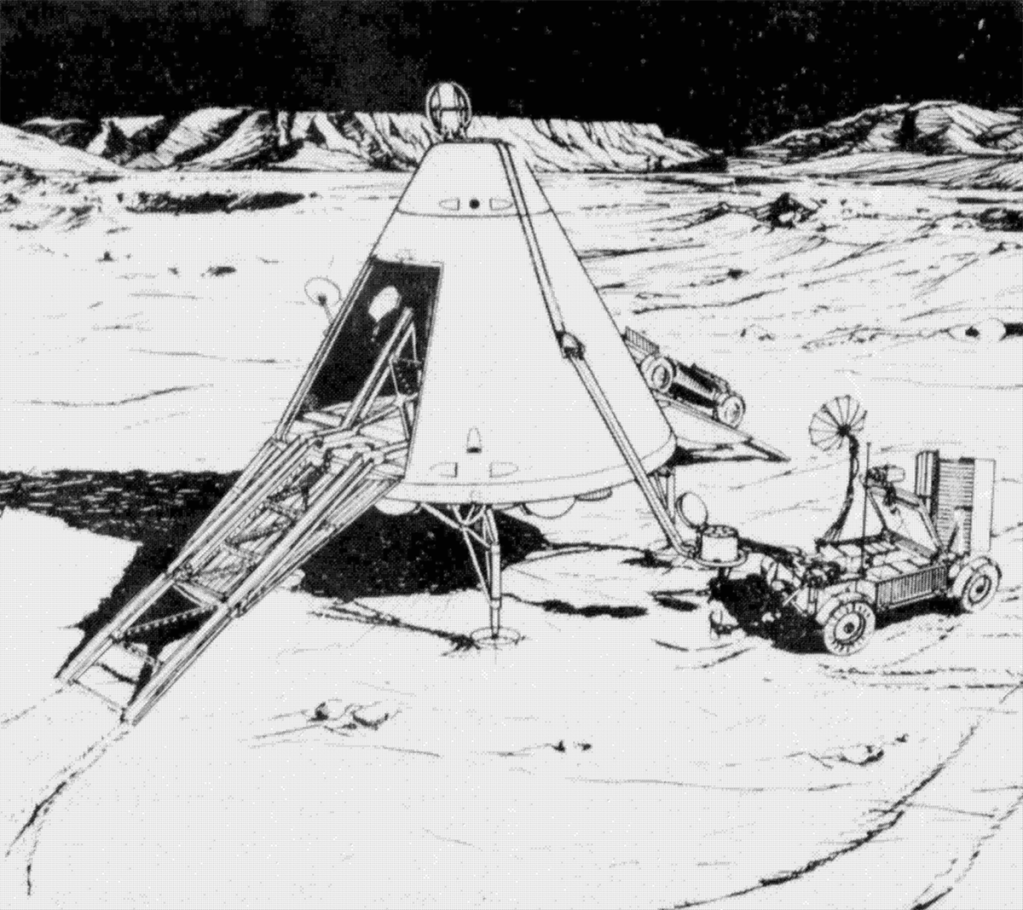
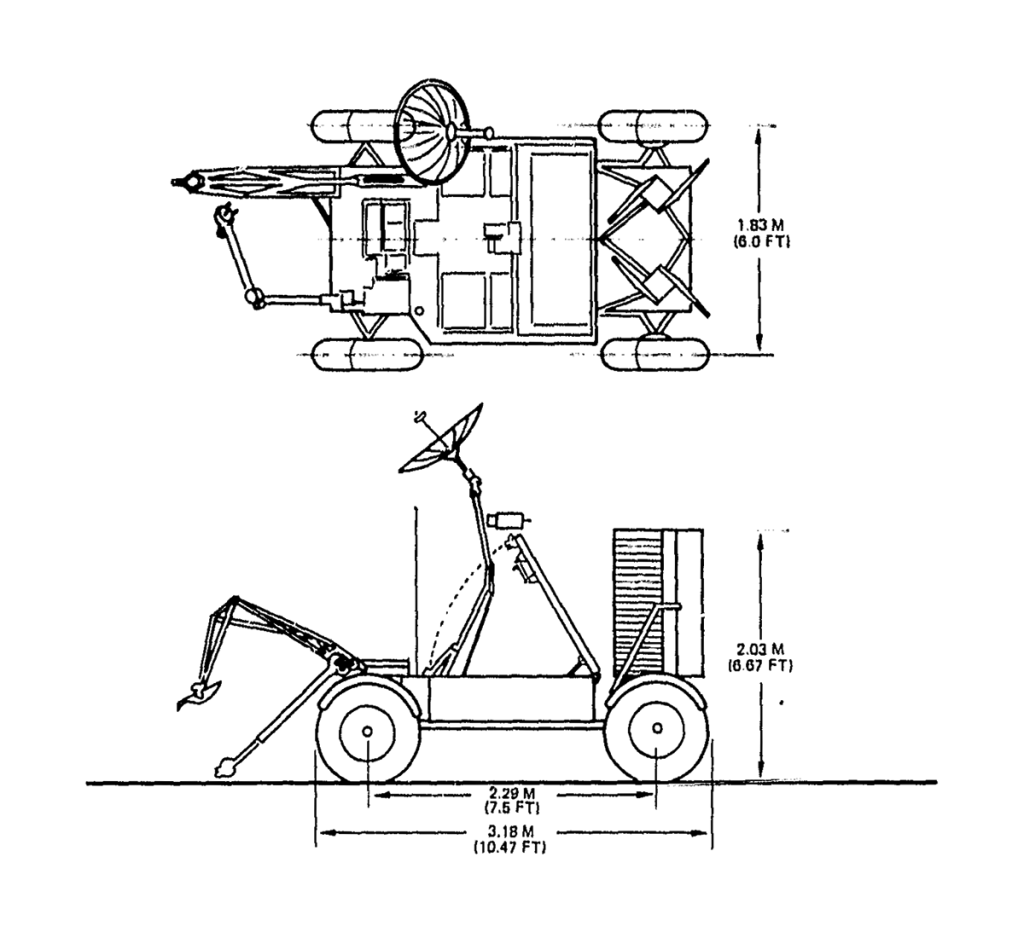
- 4-man self supporting landing
- Orbiting Lunar Station
- 8-man modular or unitary station with surface sortie
- Lunar Surface Base
- 6-man, 6 month
- 12 man, semi-permanent
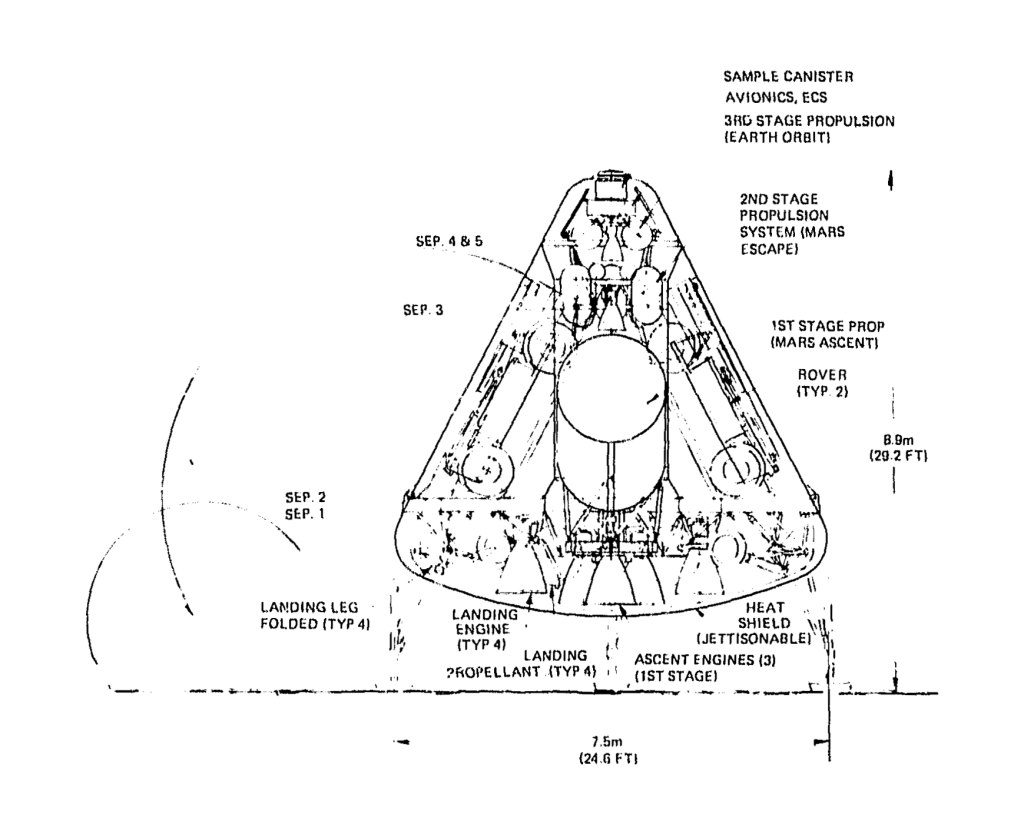
- Manned Planetary
- Manned Mars landing
- Opposition
- Conjunction
- Venus swing-by
- Manned Mars landing
- Automated Lunar
- Orbital observatory
- Backside lander
- Relay satellitr
- Automated Planetary
- Mars lander
- Jupiter atm probe
- Ganymede lander
- Nuclear Waste Disposal
- Refined waste
- Total waster
- Satellite Energy Systems
- One-orbit power generation
- On-orbit power reflectors
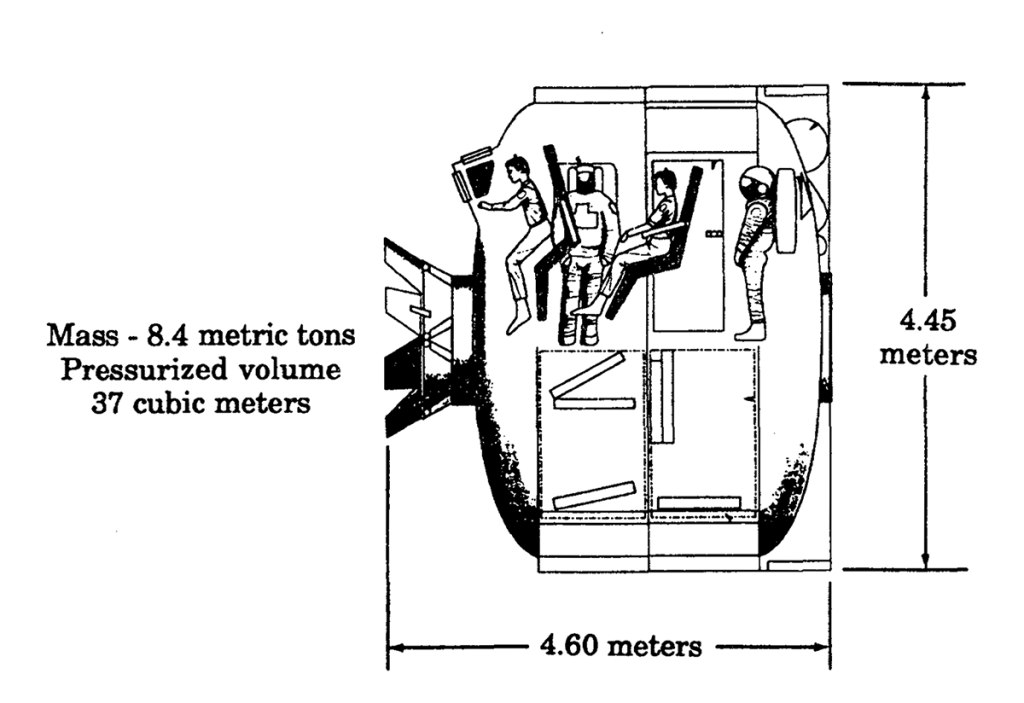
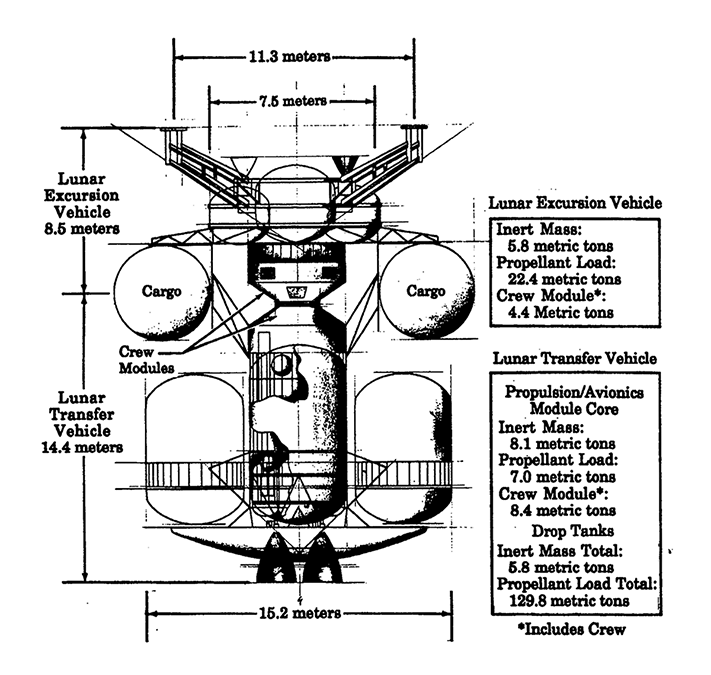
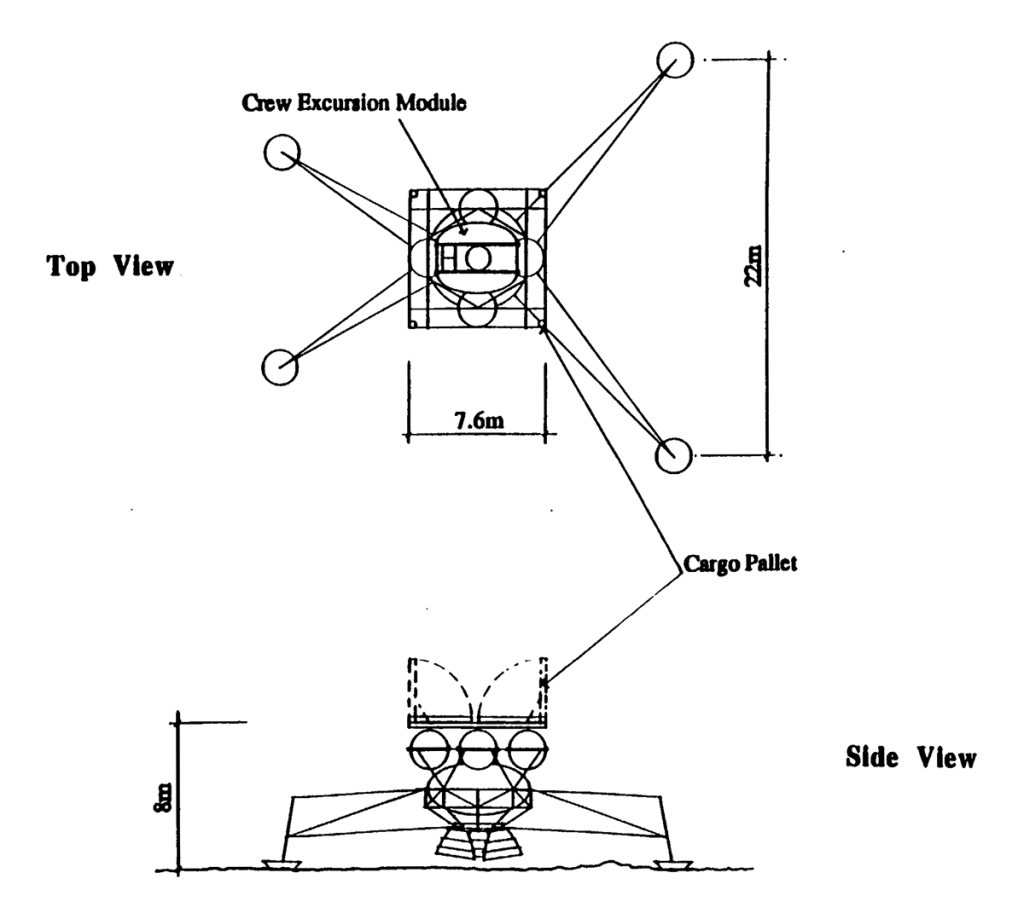
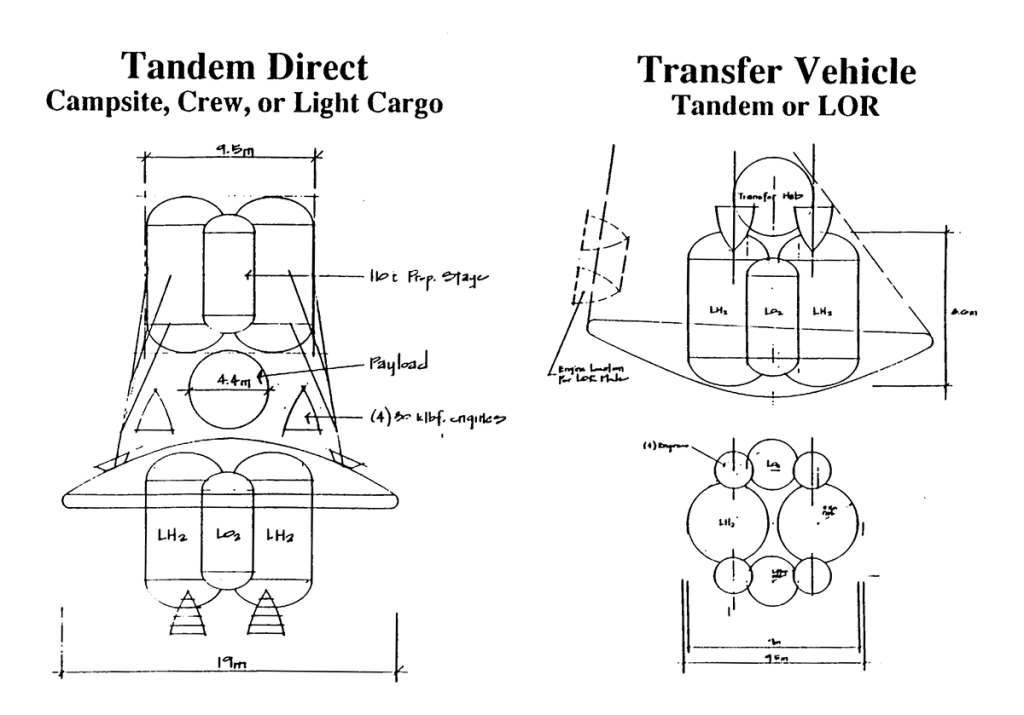
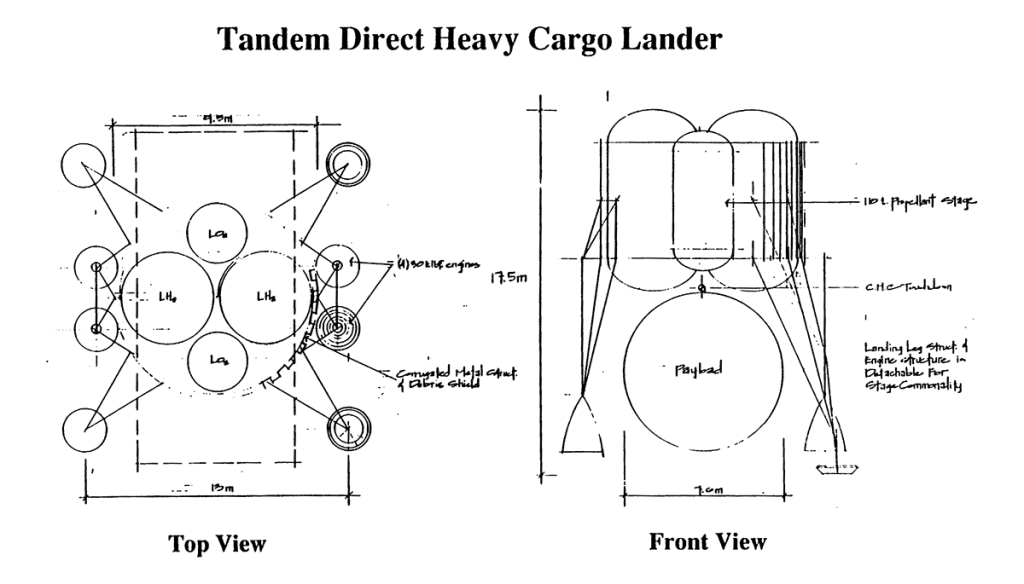
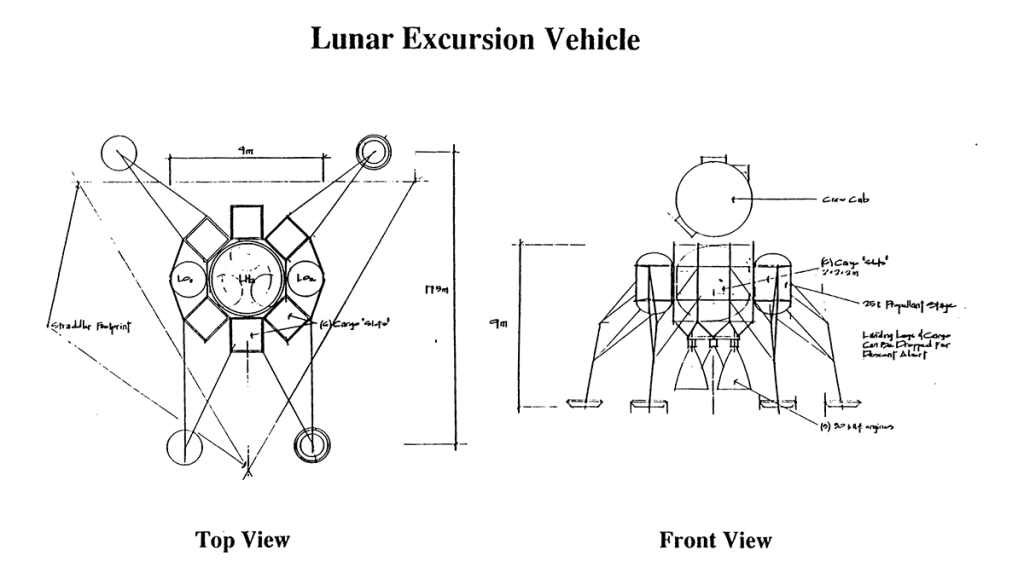
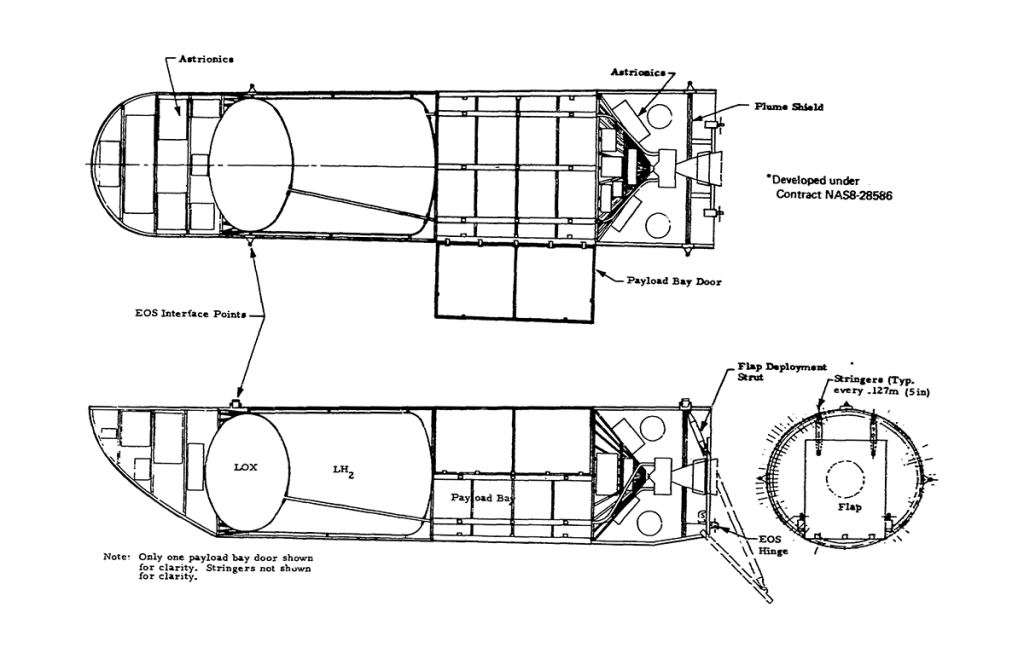
Lunar Transport Vehicles
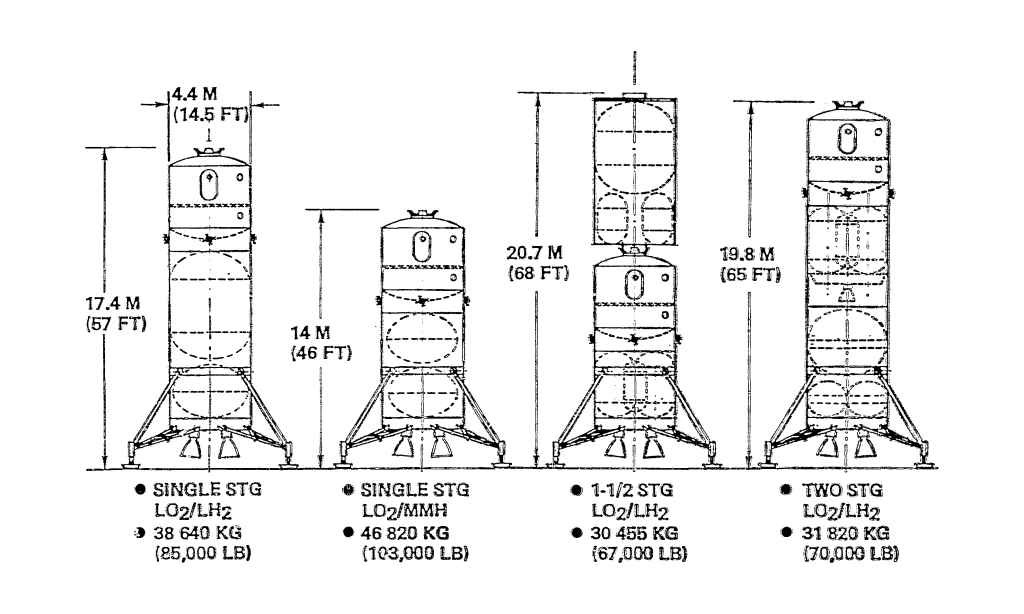
SHUTTLE COMPATIBLE
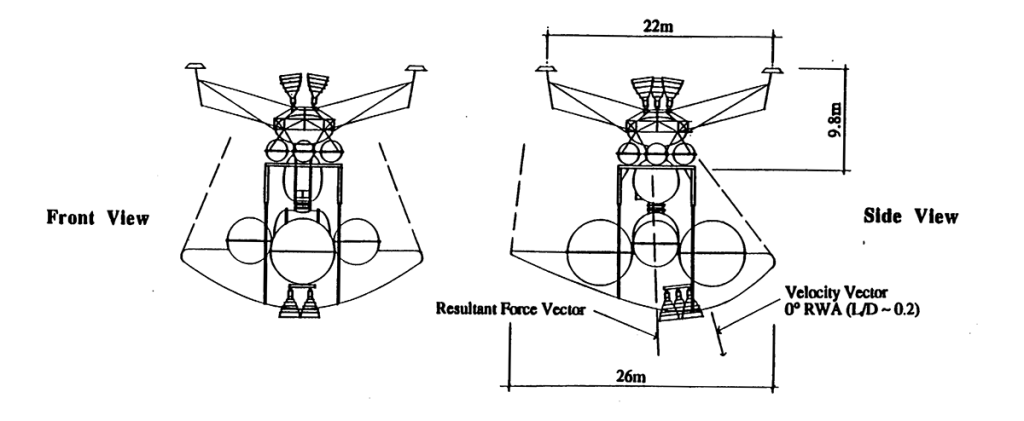
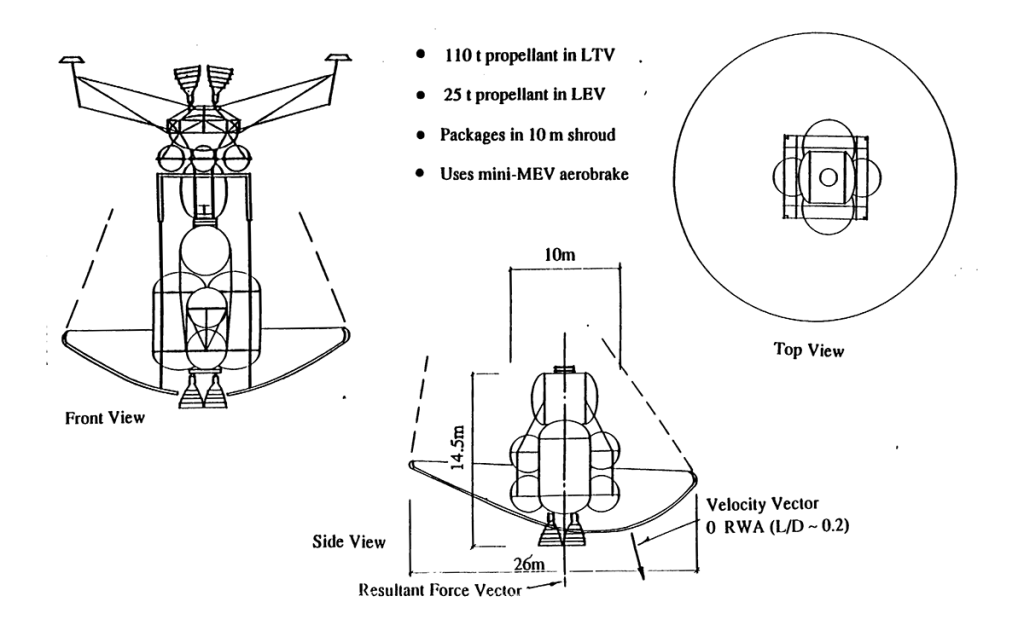
LARGE DIAMETER OTV
Earth Orbit Space Stations
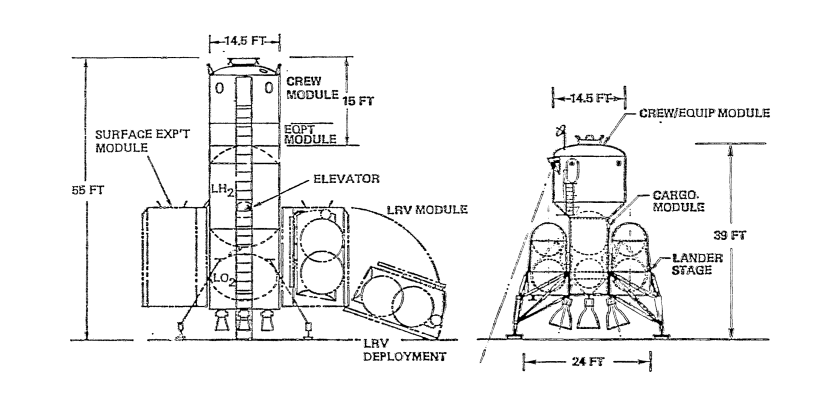
Independent Lunar Surface Space Sortie
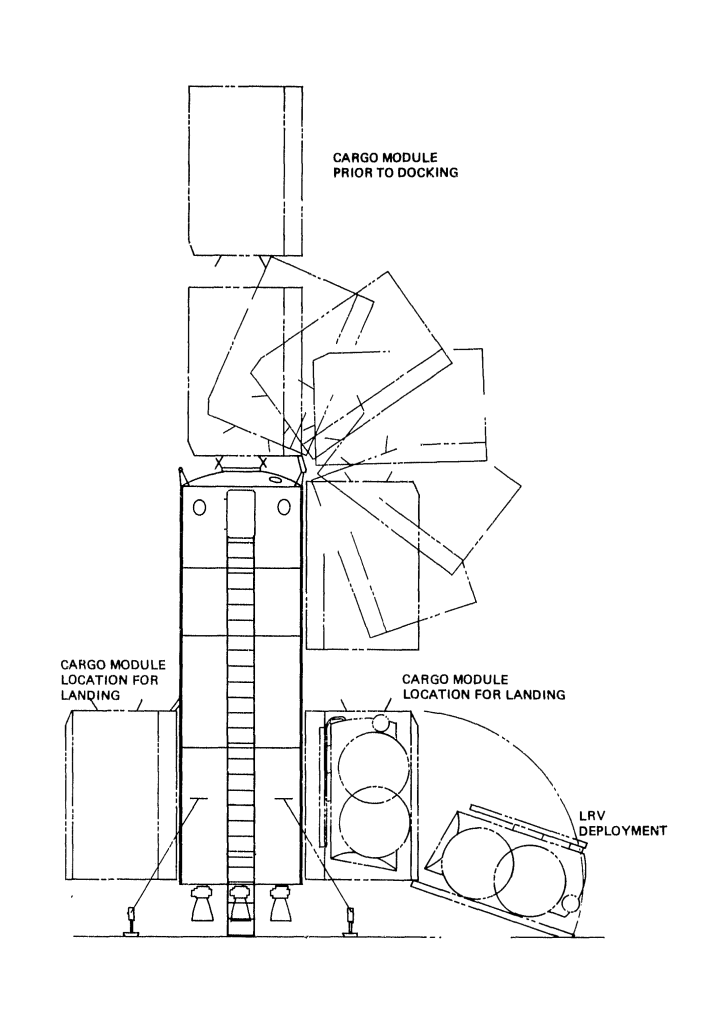
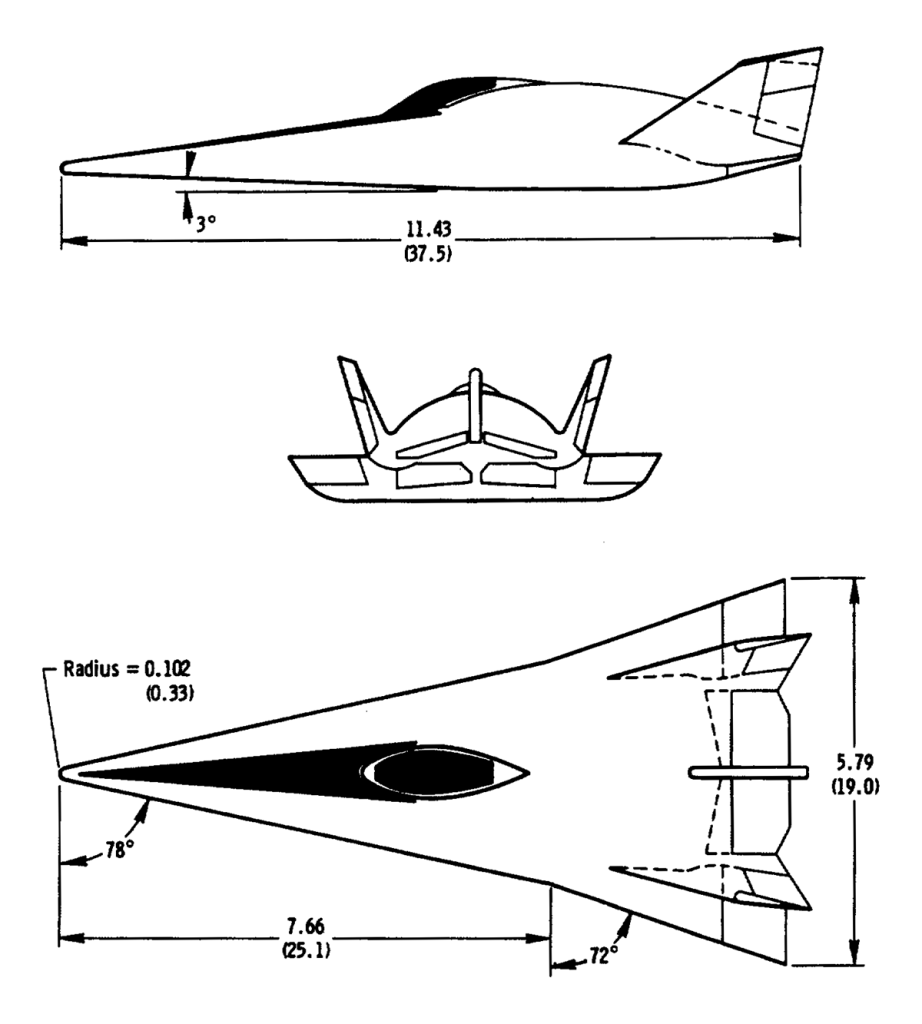
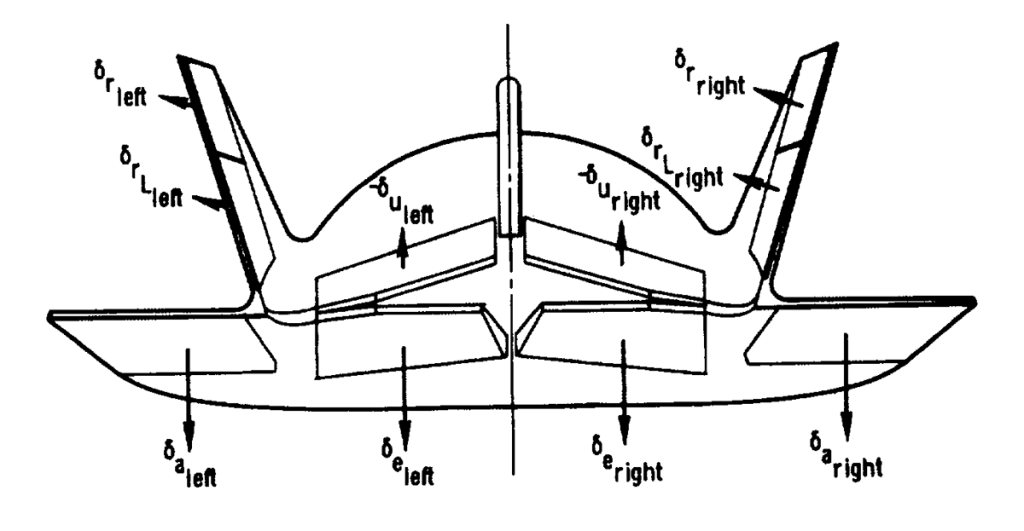
Transportation System
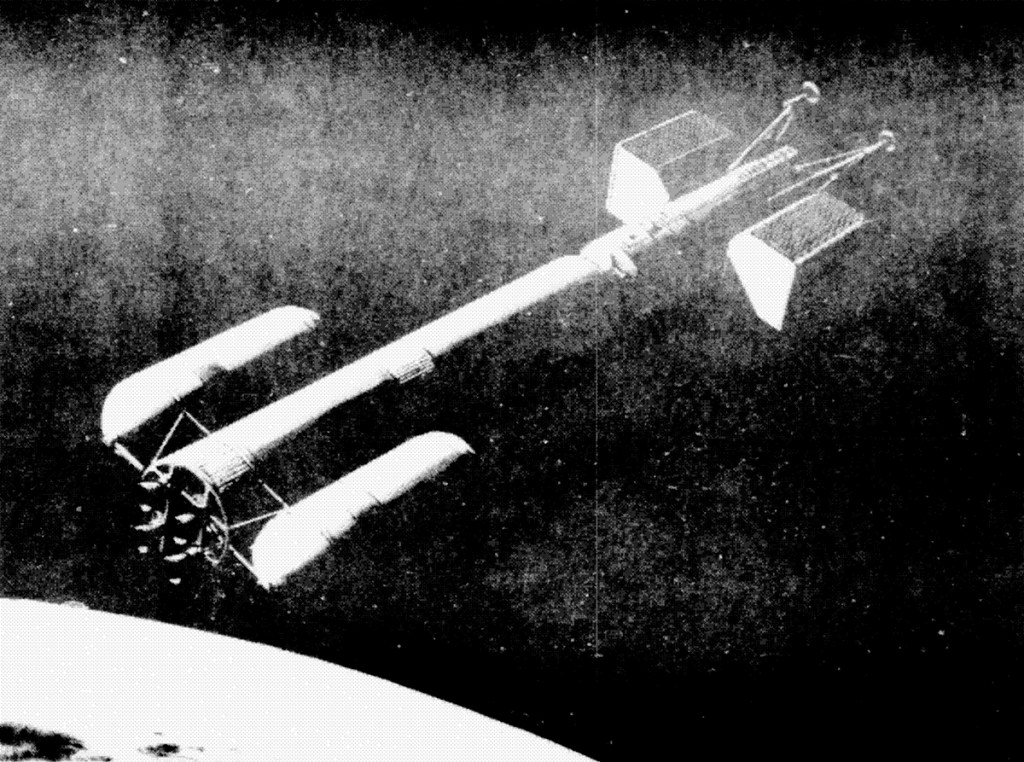
Orbiting Lunar Station
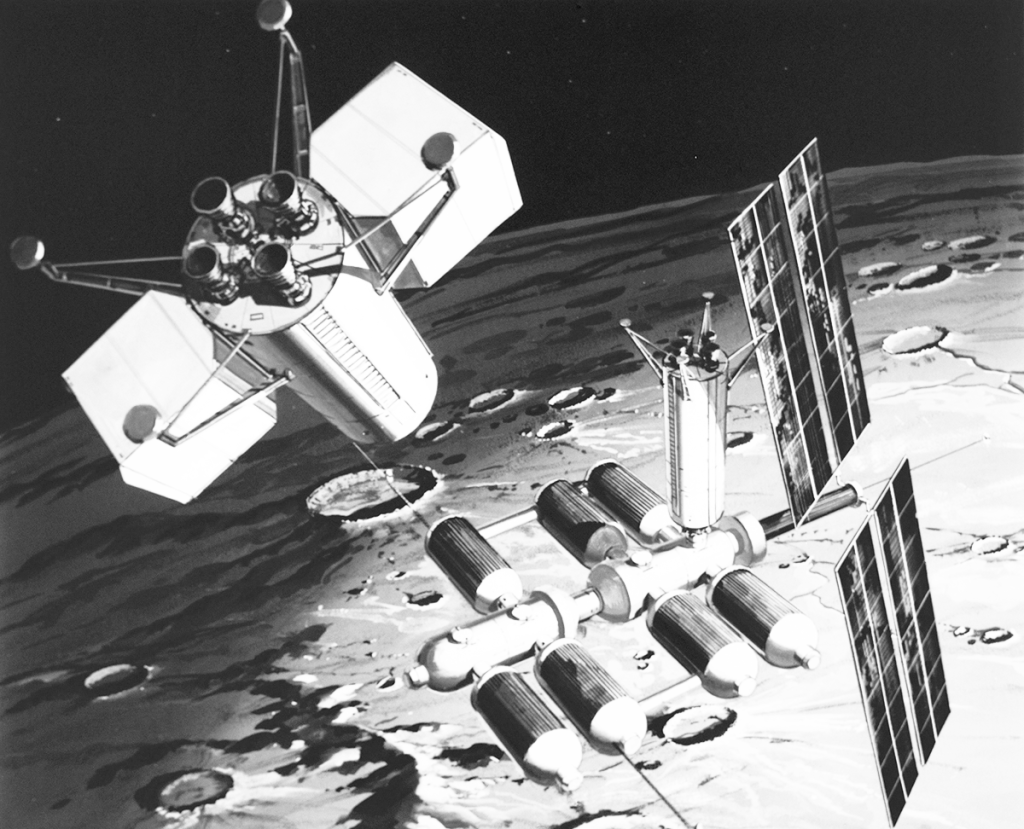
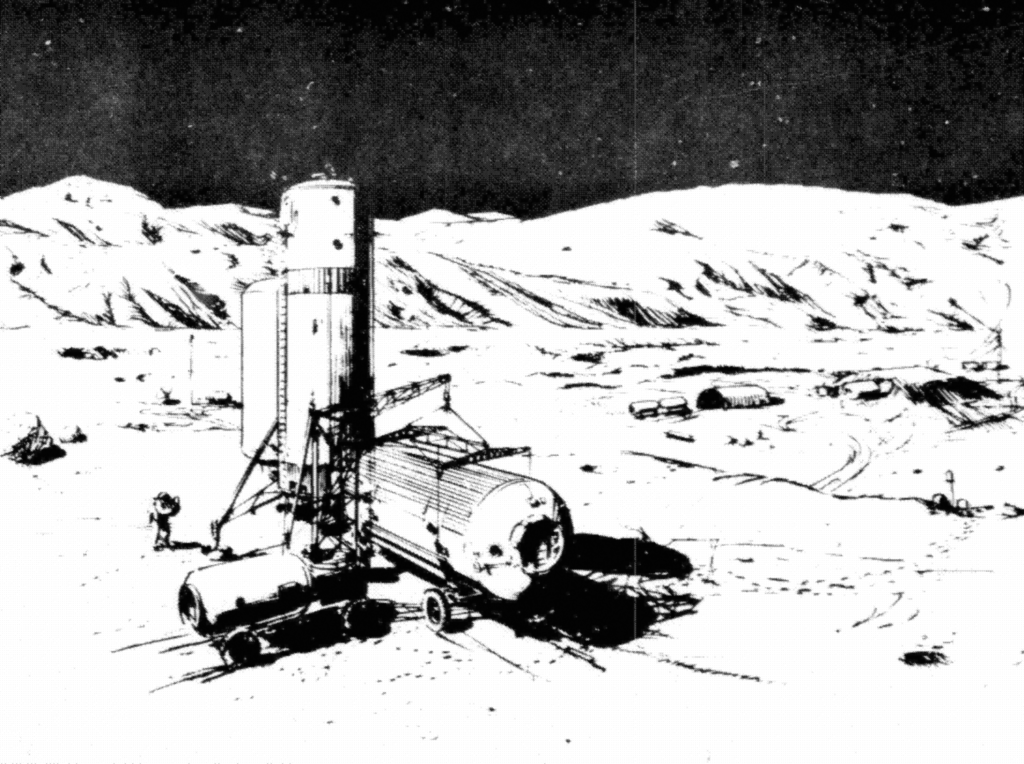
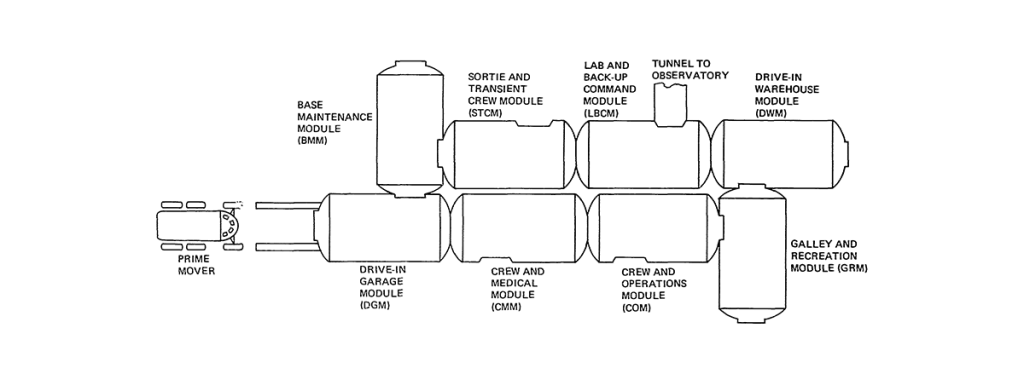
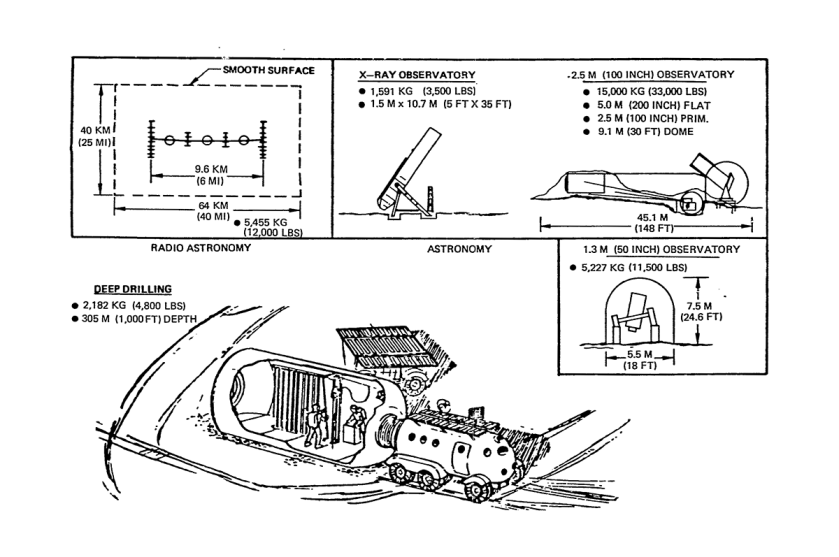
Lunar Surface Base
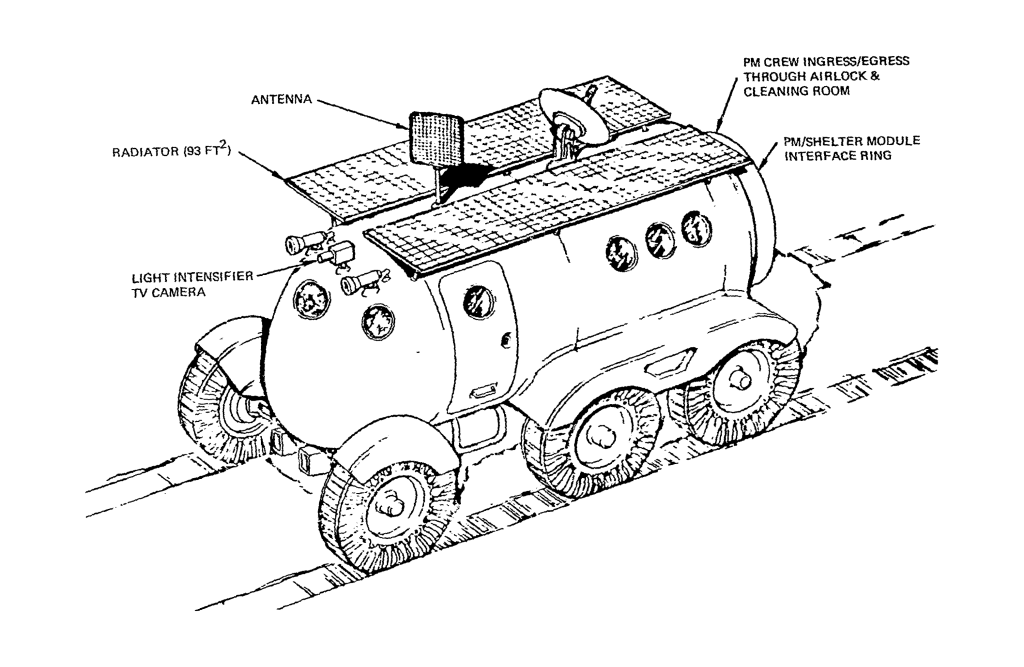
Manned Planetary Exploration Program
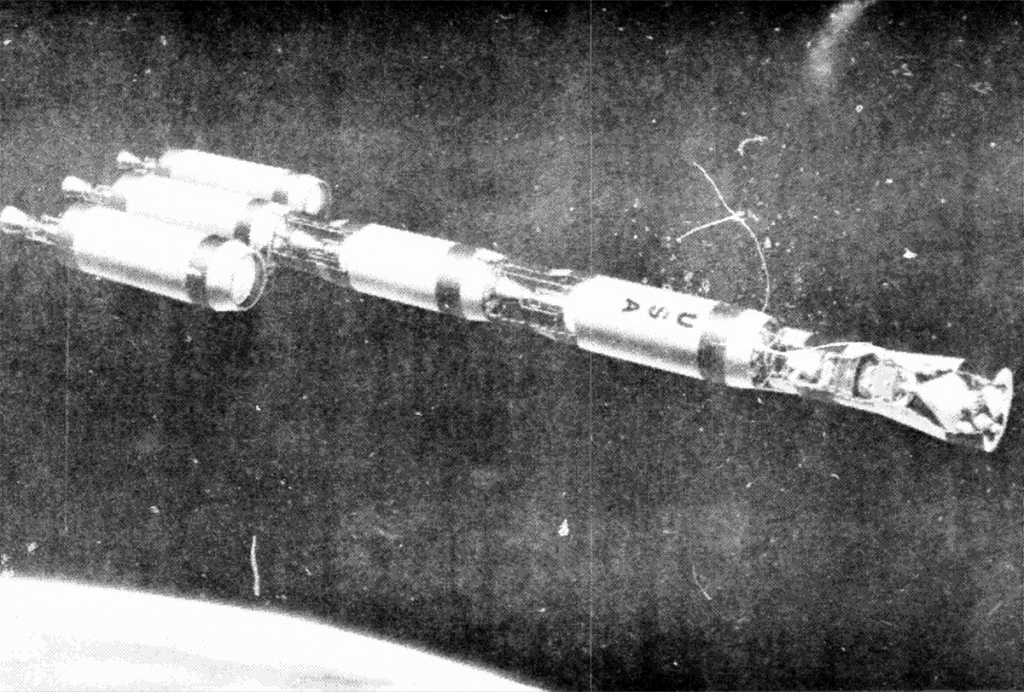
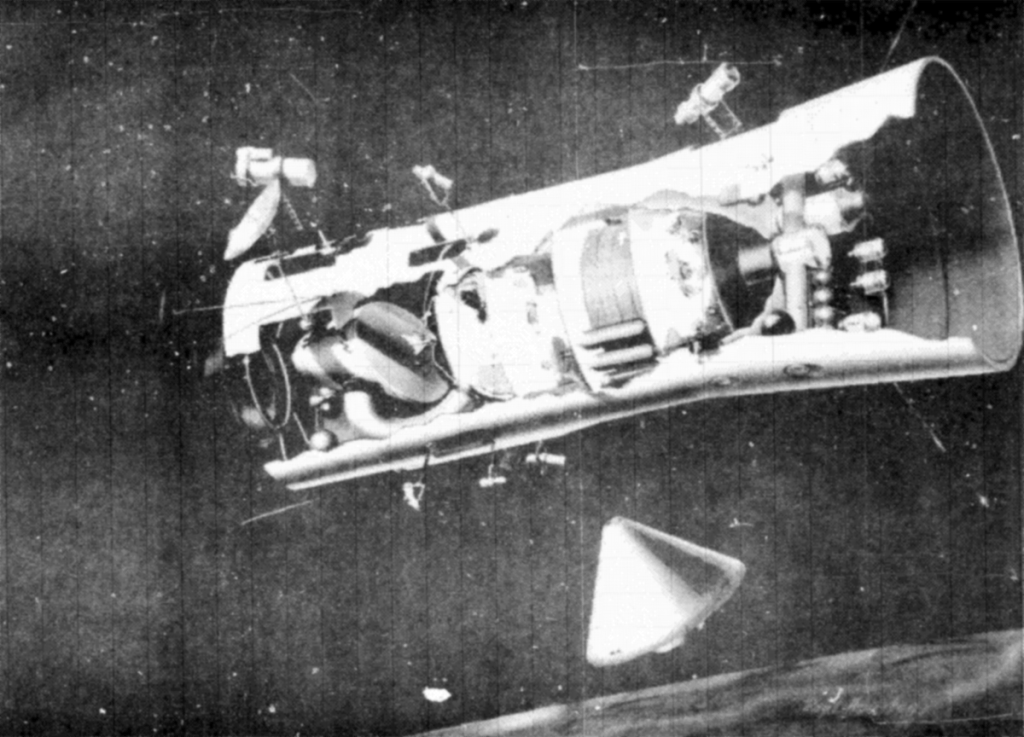
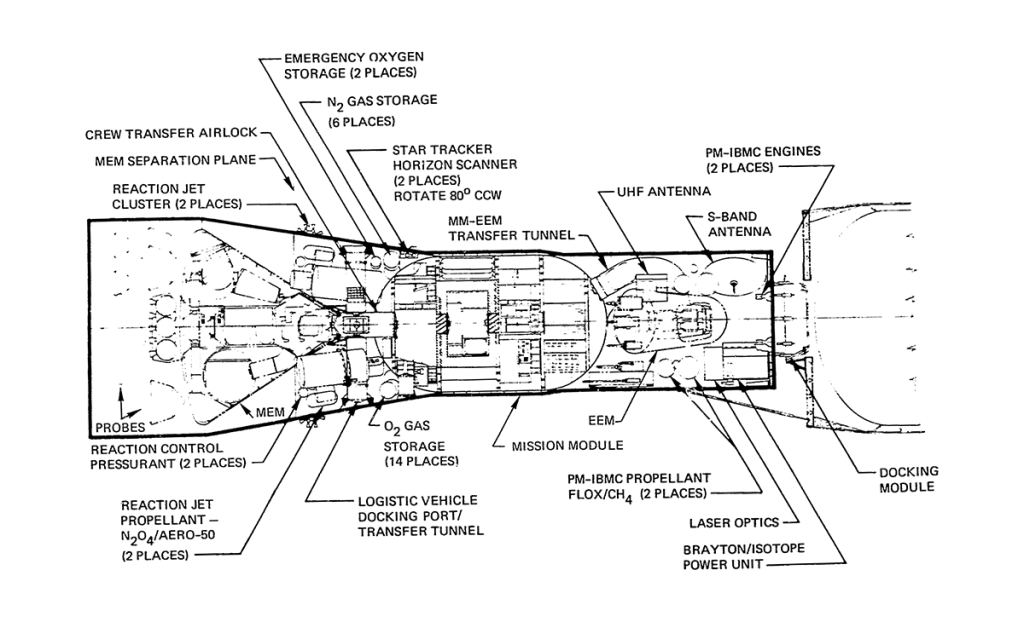
Automated Planetary Program
Satellite Energy Systems
Image credit: Boeing
File source: NASA NTRS