
Image credit: General Electric

Image credit: General Electric
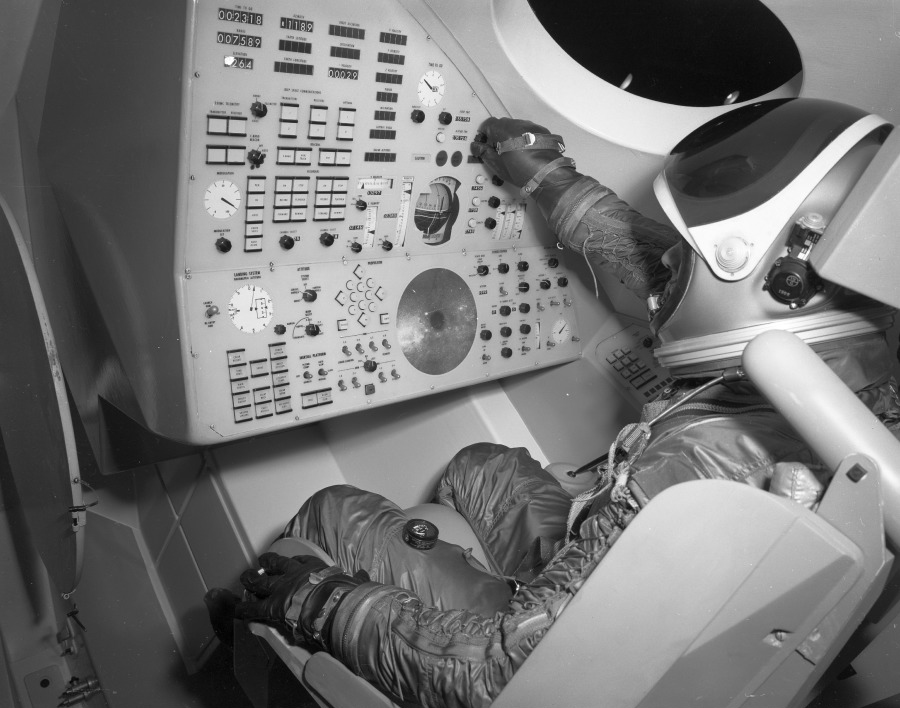
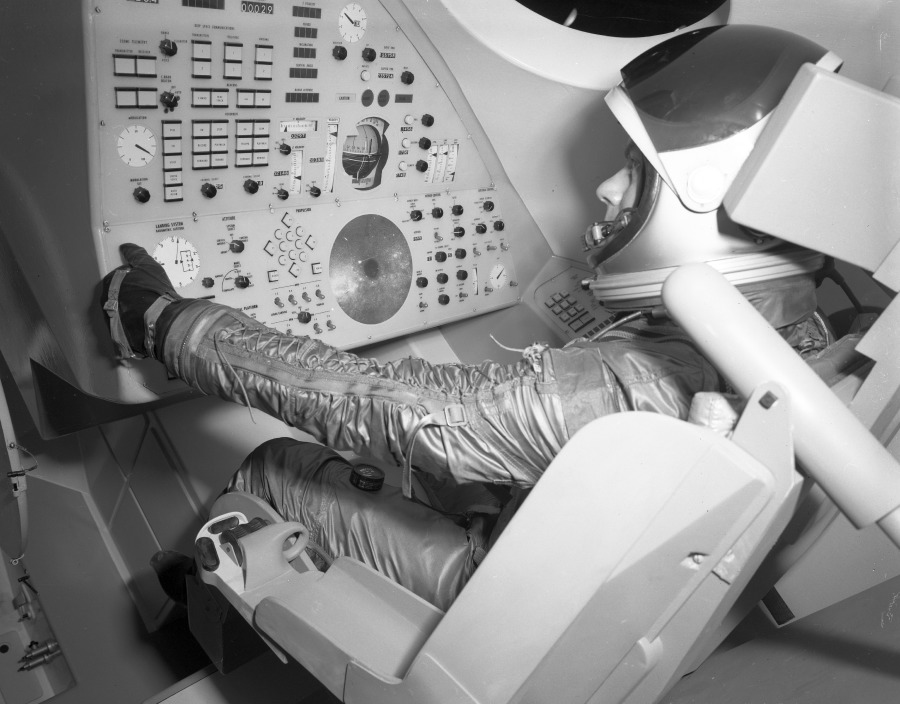
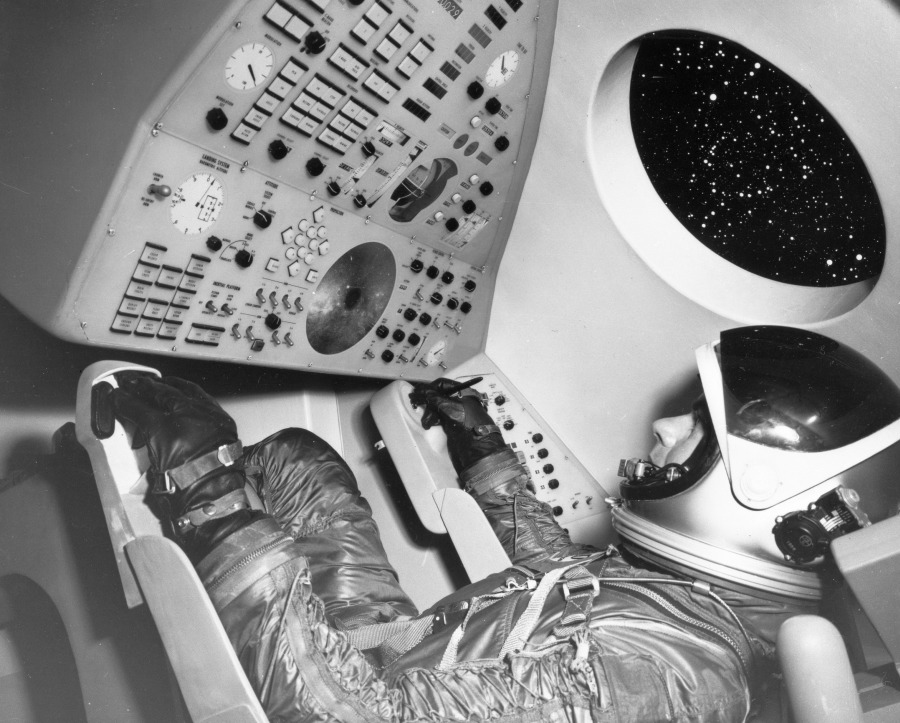




Image credit: Convair
Image source: SDASM Archives
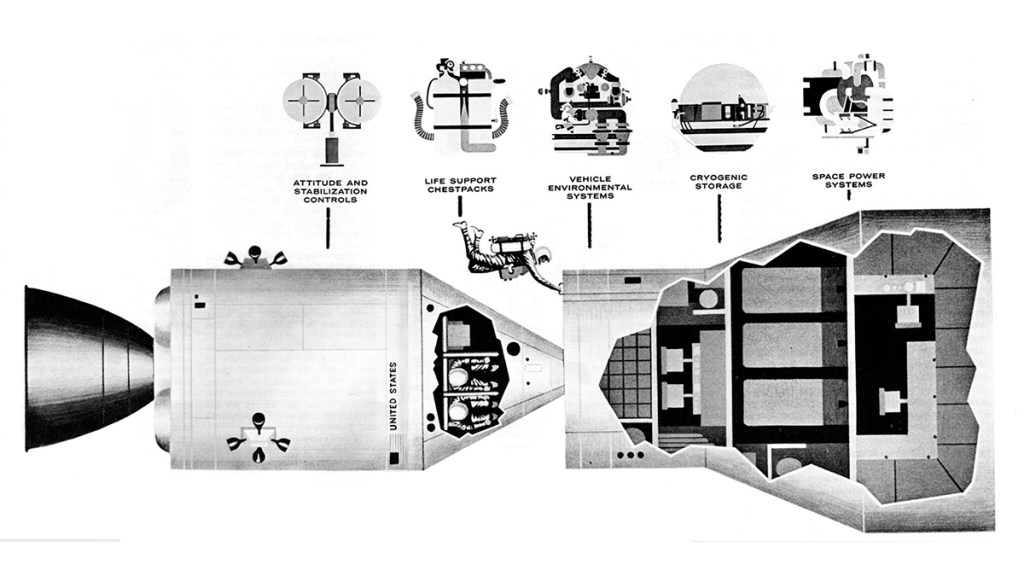
An “extended” Apollo would be able to travel for several months in space. Garrett concepts of environmental system, cryogenic storage, life-support and attitude control can be adapted to this vehicle.
Space World
December 1964, VOL. A-14
Image credit: Marquardt Corporation
Image source: Numbers Station

The Marquardt Corporation is conducting studies under contract to North American’s Space and Information Systems Division on advanced rocket reaction control systems for Apollo X. The Extended Apollo Mission is depicted above in conjunction with a space laboratory system, one of several concepts to determine additional applications of the Apollo spacecraft by NASA. Marquardt’s four-engine reaction control system cluster is illustrated above on the surface of the Apollo X service module. Similar systems are being developed by Marquardt for the current Project Apollo lunar mission on both the service and lunar excursion module.
Space World
April 1965, VOL. B-4.18
Image credit: Marquardt Corporation
Image source: Numbers Station

see also:
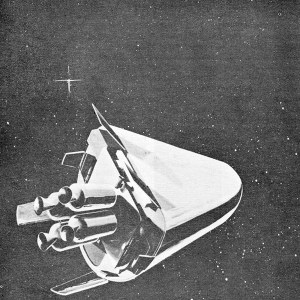
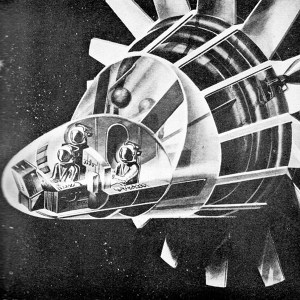
L. Apollo is pictured here by an artist of The Martin Co., one of three leading Space Age manufacturers awarded study contracts on project by NASA. Apollo was a god of Ancient Greece, son of Clymene and Titan. This is nicely appropriate, since Martin produces the mighty Titan intercontinental ballistic missile.
R. The Apollo lunar spacecraft planned to carry 3 crewmen on round trip between earth and the moon is shown above here enroute among the stars. Protruding fan-shapes are solar arrays to gather energy from sun for use aboard. Apollo was said to have been the triumphant participant in Olympic games. Homer called him the “god of prophecy.”
America’s Mightiest Missile
by Larry Eisinger
Arco Publishing, 1961
Image credit: NASA
Image source(s): Mike Acs, Numbers Station

Image credit: North American Aviation
Image source: DVIDS

Image credit: Teledyne Ryan Aeronautical
Image source: NASA Images

Image credit: Ryan Aeronautical
Image source: Mike Acs