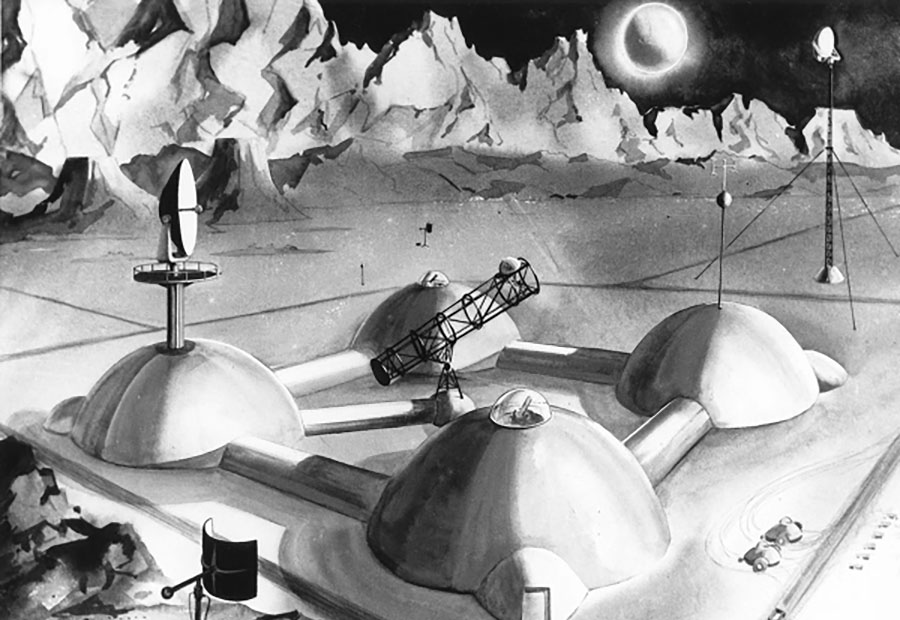
Our World in Space
Robert McCall & Isaac Asimov
New York Graphic Society, 1974
Image credit: Robert McCall
Image credit: NASA
Image source: Numbers Station
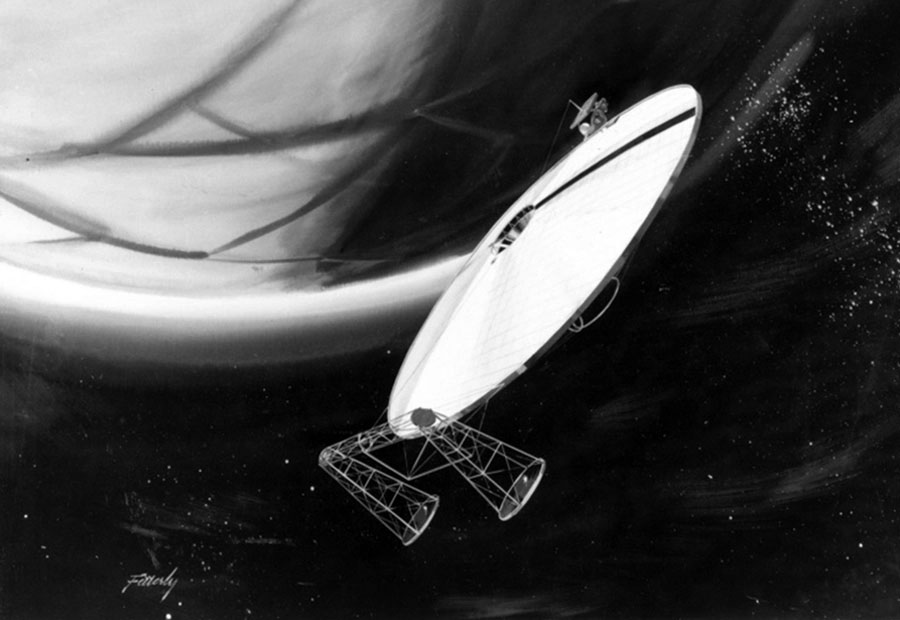
Our World in Space
Robert McCall & Isaac Asimov
New York Graphic Society, 1974
Image credit: Robert McCall
Image credit: NASA
Image source: Numbers Station

NOV 1 1972
THIS SPACE SHUTTLE IS SCHEDULED TO START OPERATIONS IN 1978
Vehicle will make round trips ferrying men into orbit and the returning them to earth.
Image credit: North American Rockwell
Image source: Numbers Station

Third release week of November 15, 1971
THE 6:10 INTO SPACE. NASA is working on the design of a winged shuttle craft to resupply the manned space stations of the next decade. The giant space transports shown here can carry 50,000 pounds of men and cargo to the cluster of cylinders that make up a space base, the return to Earth and land like airplanes.
Credit: North American Rockwell
Image credit: North American Rockwell
Image source: Numbers Station
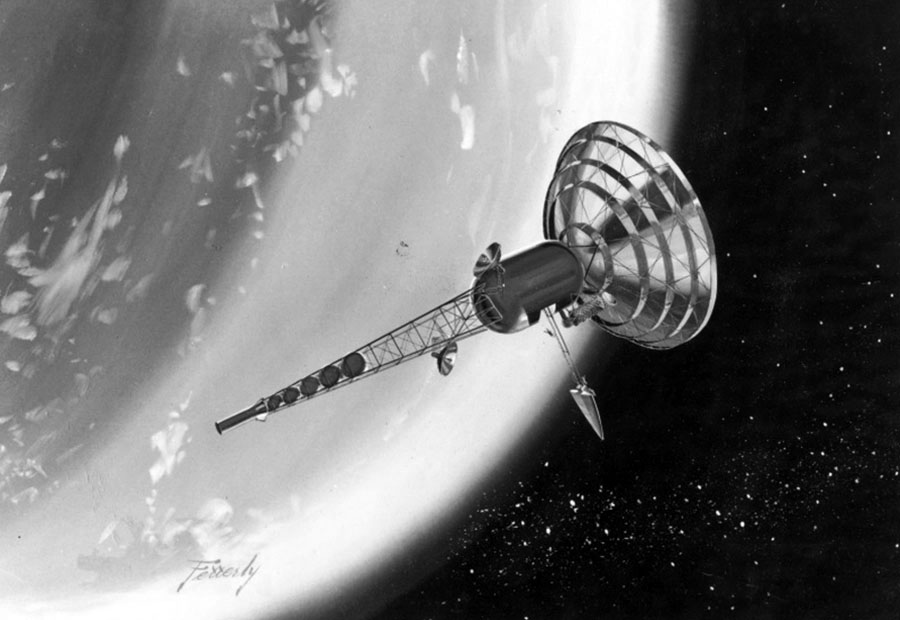
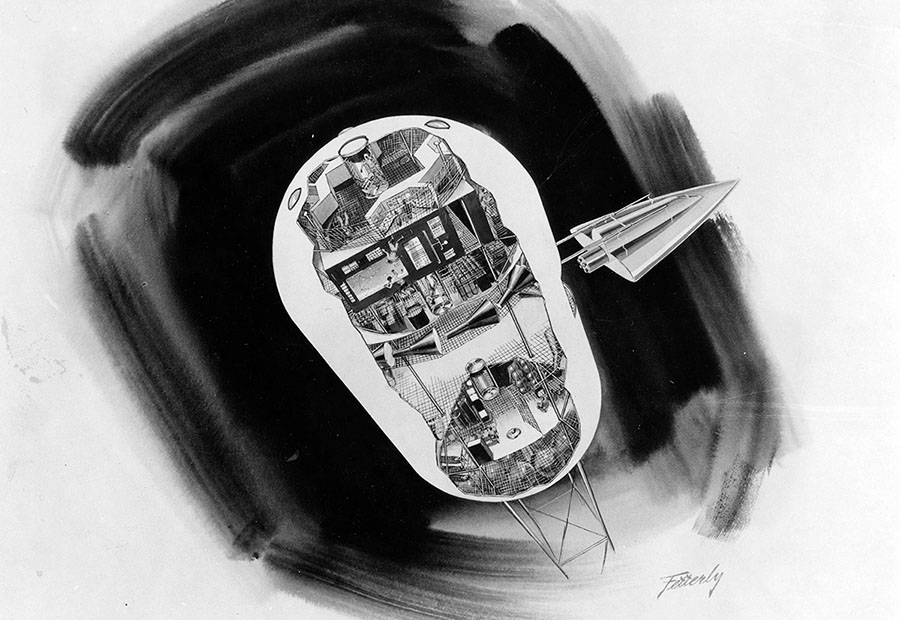
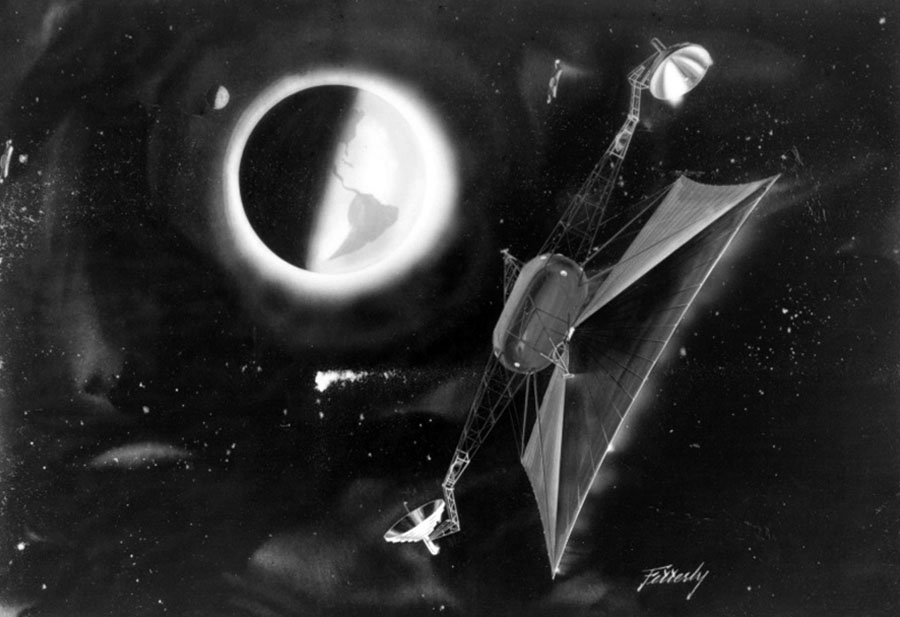
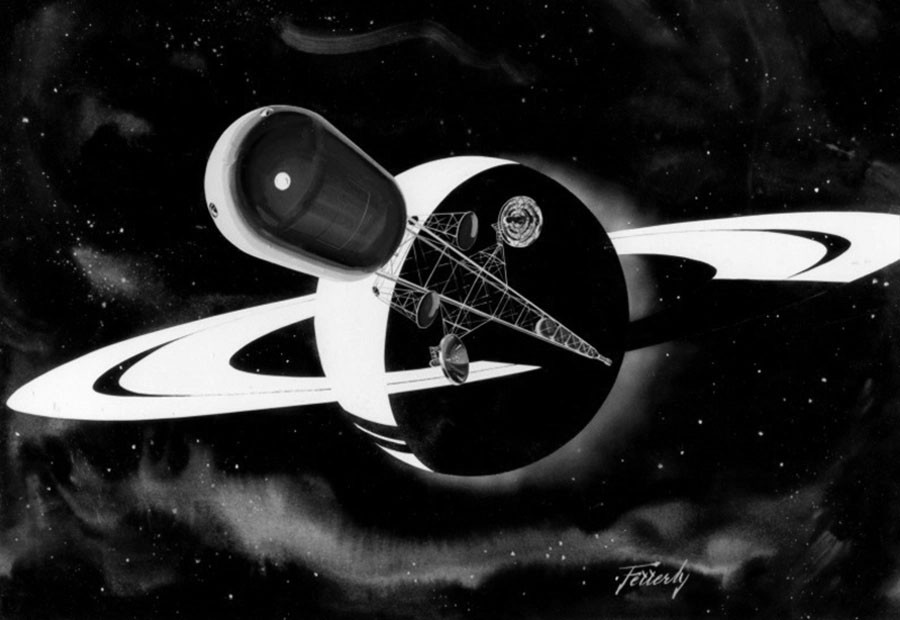





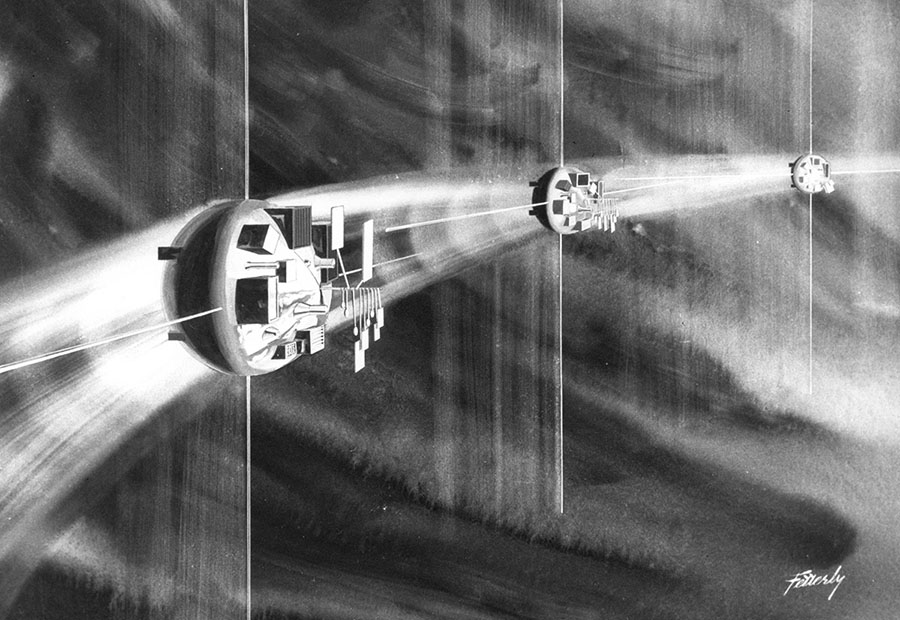
In the late fifties the Boeing Aircraft Company conducted an exhaustive study that culminated in what they called the Program for Astronomical Research and Scientific Experiments Concerning Space. In essence, PARSESCS was a roadmap to a future in space that begins with manned spaceflight in earth orbit and ends with human exploration of other worlds.
Boeing released a number of reports relating to PARSECS, notably one that accompanied a talk given by (then) SVP Wellwood E. Beall at the Commodore Hotel in New York in April, 1960 for the Society of Automotive Engineers. In the accompanying paper, Beall says: “The program has the general objective of providing a focus for Boeing personnel engaged in space-oriented research not directly associated with military programs. Specifically it tabulates requirements for space research drawn from many sources and then defines the vehicles and systems to accomplish the resultant broad scope of objectives.”
If you’re yearning for more information, I’ll suggest this thread on Secret Projects Forum. The technical paper that accompanied Beall’s SAE presentation can be downloaded here.
PARSECS MISSIONS
Mission I – Earth Satellite Observatory
Mission II – Moon Colony
Mission III – Counter Moon
Mission IV – Interplanetary Probes
Mission V – Close Solar Orbit
Mission VI – Trojan-Point Observatories
Mission VII – Out-Of-Ecliptic-Orbit
Mission VIII – Planetary Exploration
Image credit: Boeing Aircraft Company
Images: Mike Acs, SDASM Archives
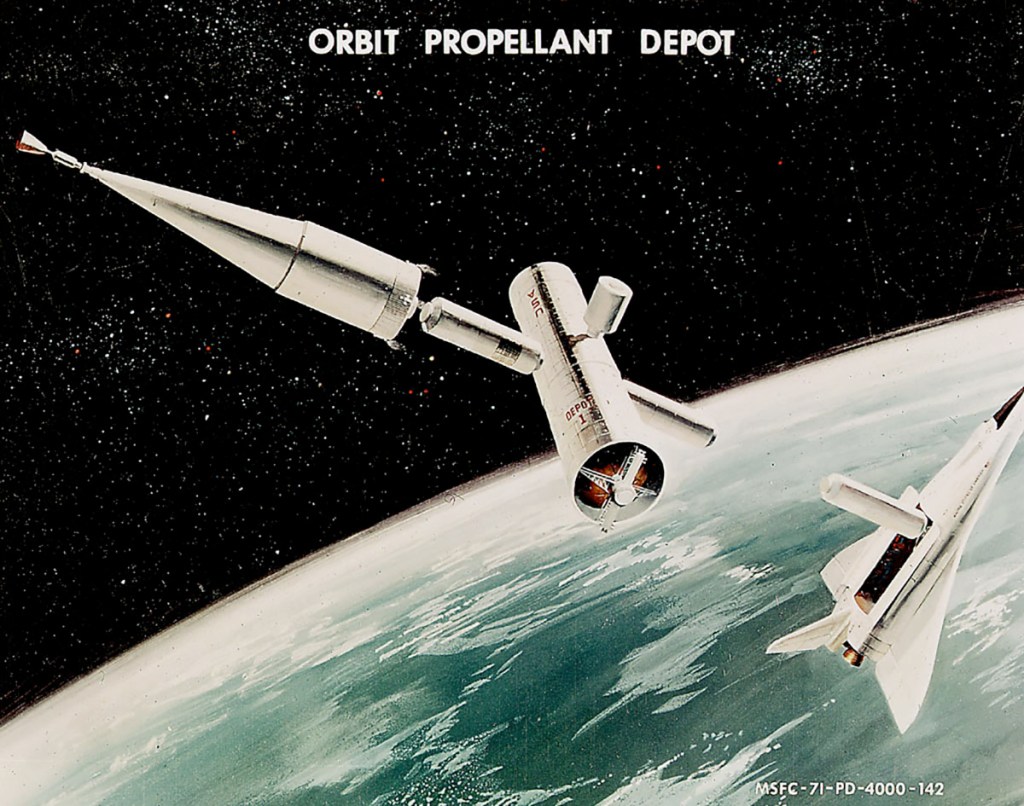
Image credit: NASA MSFC
Image source: NASA Marshall
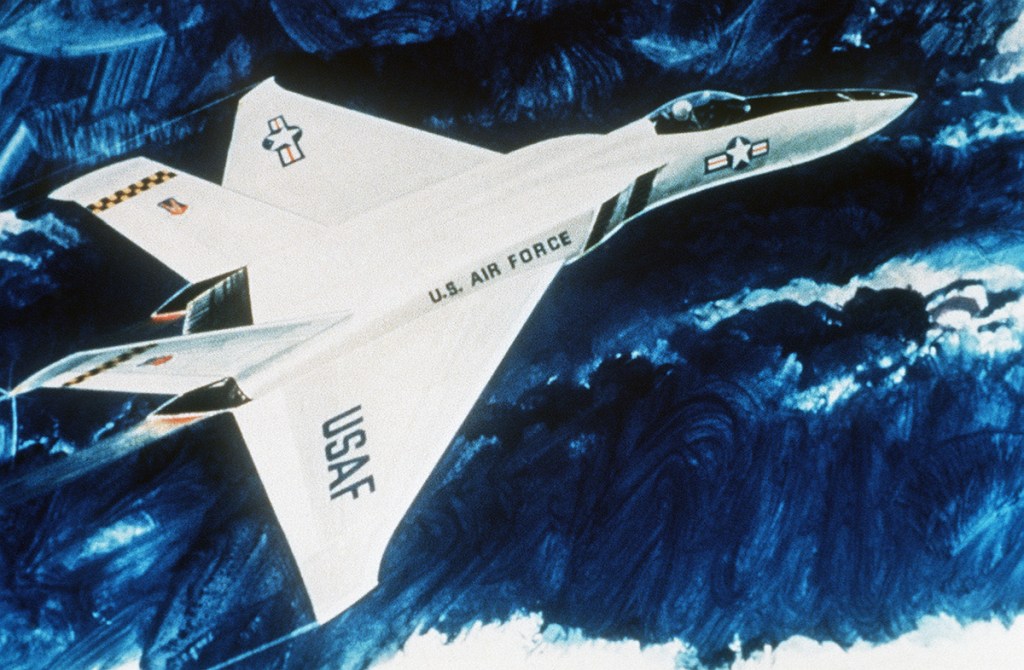

Image credit: Northrop
Image source: National Archives

This illustration depicts a side view of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth’s atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
Image credit: NASA KSC
Image source: NASA Images