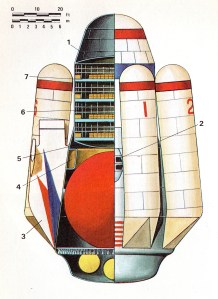
Pegasus Intercontinental Passenger Rocket
- Forward pressure dome;
- Two-man crew compartment;
- Re-entry stabilization fines (2);
- Cargo compartment;
- Aft pressure dome;
- Pressurized cabin for passengers (170);
- Deck structure (4) with passenger couches (43 each).

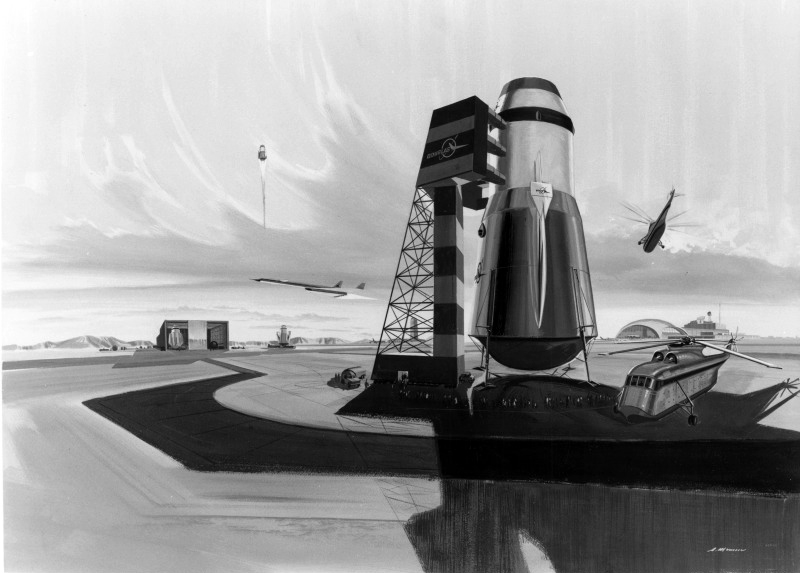
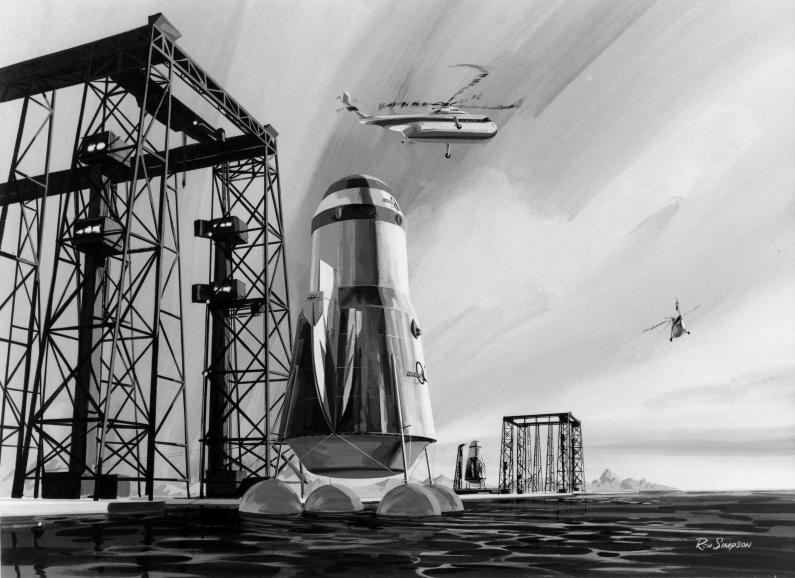
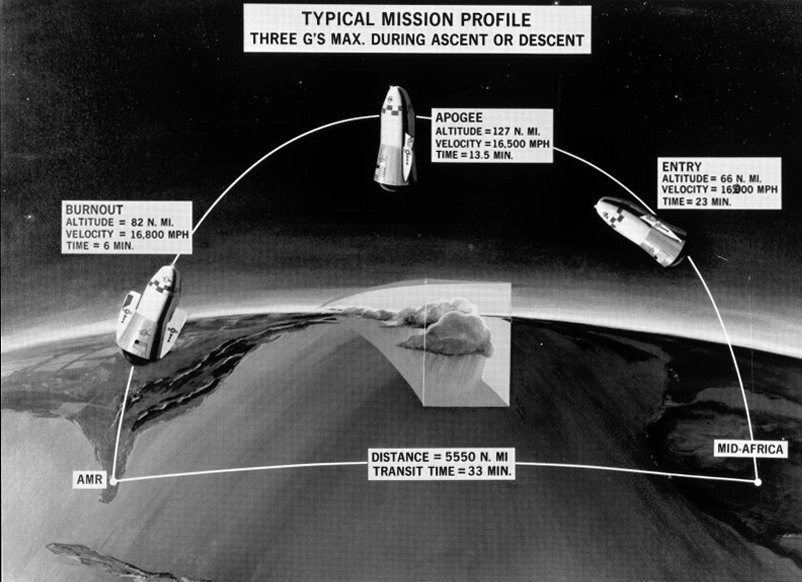
Pegasus during atmospheric re-entry uses the LH2-cooled plug nozzle as a heat shield. The ballistic transport would convey 172 passengers and freight 7,456 miles (12,000 km.) in 39 min. without exceeding an acceleration of 3g during ascent or re-entry. At the arrival spaceport it would hover on rocket thrust during a soft landing in the vertical attitude.

Pegasus Passenger Compartment
- Four-level passenger access doors (3);
- Stairways (2) connecting four passenger decks;
- Double-wall acoustic damping structure;
- Luggage racks (9);
- Re-entry stabilization fins (2).
Frontiers of Space
Philip Bono & Kenneth Gatland
Macmillan, 1969
Image credit: Douglas / Blandford Press
Images: Numbers Station, SDASM Archives