see also:

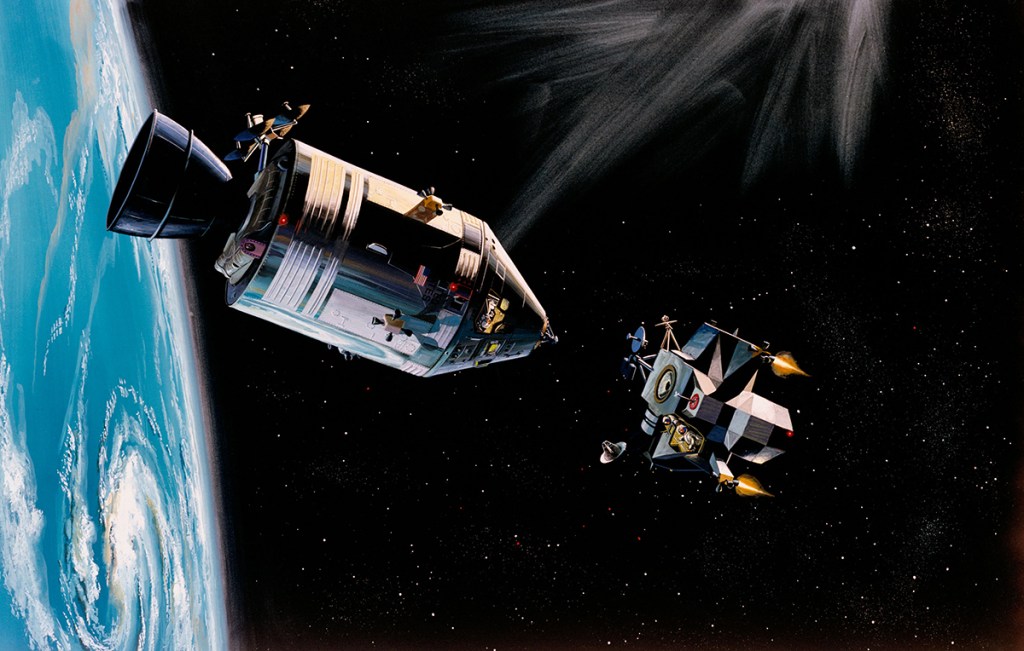
It took me a few, but the lower version is either an earlier or later version of the same painting. The figure representing James B. Irwin is a repaint. My guess is the image on NASA’s site is later, reworked to give the figure a slightly more dramatic pose. The painting is by a North American Rockwell artist.
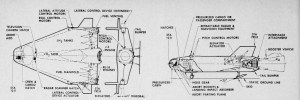
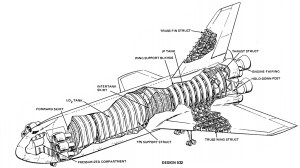
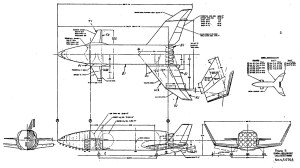
Image credit: NASA JSC
Images: NASA Images, Numbers Station