
Image credit: NASA
Image source: Mike Acs




Space World
December 1964, VOL. A-14
Image credit: Douglas
Image source: Numbers Station


How We Will EXPLORE THE MOON
Mechanix Illustrated, June 1959
Image credit: Mechanix Illustrated
Image source: Internet Archive


More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

The unloading on the moon. Twenty-four hours after landing, supplies have been stowed in caterpillar tractors. Hold of cargo ship (r.) is being lowered to ground in sections, to be used as prefabricated headquarters, Earth is at center; halo effect is caused by sun, hidden behind sphere of rocket ship at left. Diagonal streak in sky, the zodiacal light, is caused by sun’s ray reflecting from cosmic dust. The red star at left is Mars.
More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston

Causing moonquakes. Rockets with explosive war heads are fired off and scientists check the vibrations waves caused by distant blast, to determine interior composition of the moon. Seismograph in foreground is push-button controlled and surveying instrument to it’s left has cupped headpiece, to accommodate hooks and helmets of expedition members.
More about Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 25, 1952
Image credit: Collier’s
Image source: AIAA Houston
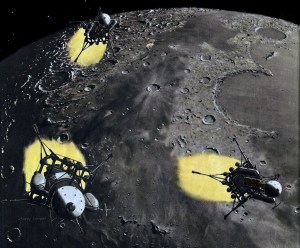
Landing on the moon. Ten minutes before touchdown, rocket motors are switched on to slow down ships’ high-speed fall caused by the moon’s gravity. Vehicles are maneuvering 550 miles above landing area known as Sinus Roris (Dewy Bay), dark plain above cargo ship in lower left.
Man on the Moon
Collier’s, October 18,1952
Image credit: Colliers
Image source: AIAA Houston
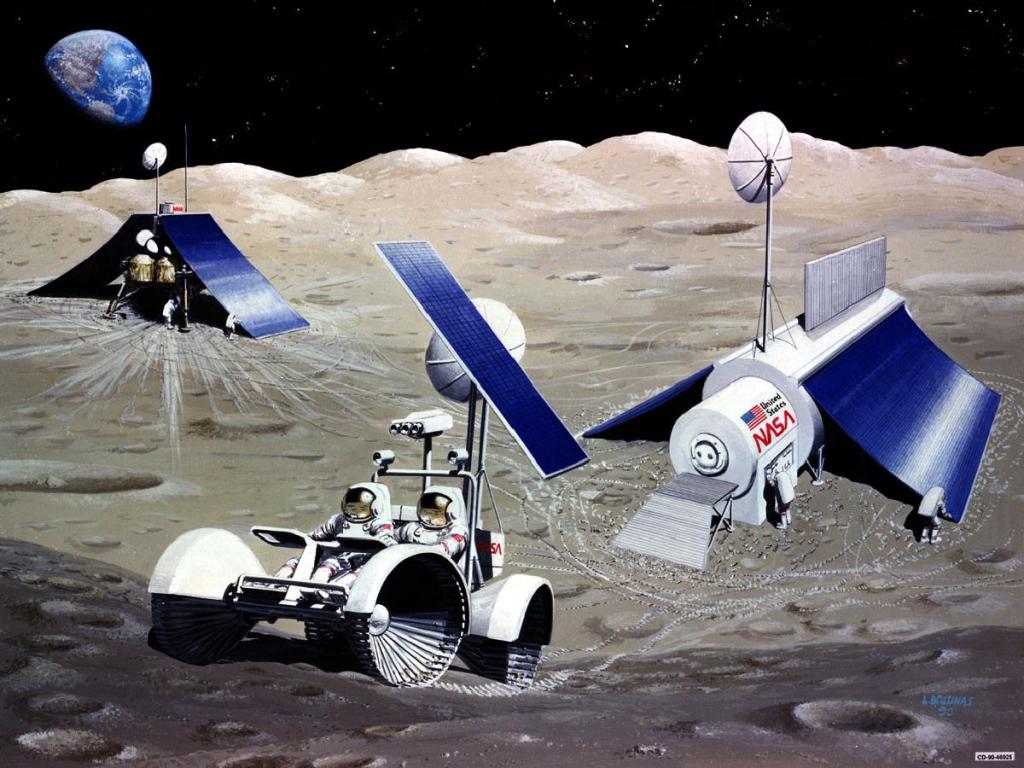
Image credit: NASA LRC
Image source: NASA Images

S83-28321 (14 March 1983) — In this artist’s concept of future lunar operations, a lunar ferry is about to burn out of lunar orbit for the trip back to facilities in low Earth orbit. The ferry vehicle carries tank modules filled with liquid oxygen, which has been produced from mining operations on the surface of the Moon. One possibility for such operations would be to have manned facilities in low lunar orbit, such as illustrated here. At the upper right side of the photo is a small orbiting manned station. At the lower right side of the photo is a liquid oxygen propellant dump, to which a lunar landing vehicle carrying liquid oxygen is about to dock. The lunar ferry vehicle itself is representative of one type of aerobraking system. The balloon-like torus around the center of the ferry-craft would inflate to several times its illustrated size and, once the vehicle has swooped down close to the Earth’s outer atmosphere on the return journey, would use atmospheric drag to slow the craft and place itself in low Earth orbit. The liquid oxygen would then be used in operations there for fueling various vehicles, including an orbital transfer vehicle for trips to geosynchronous Earth orbit. This concept is part of a study done for the Johnson Space Center by Eagle Engineering of Houston. The artist was Pat Rawlings.
Image credit: Eagle Engineering
Image source: Internet Archive

Image credit: NASA GRC
Image source: National Archives