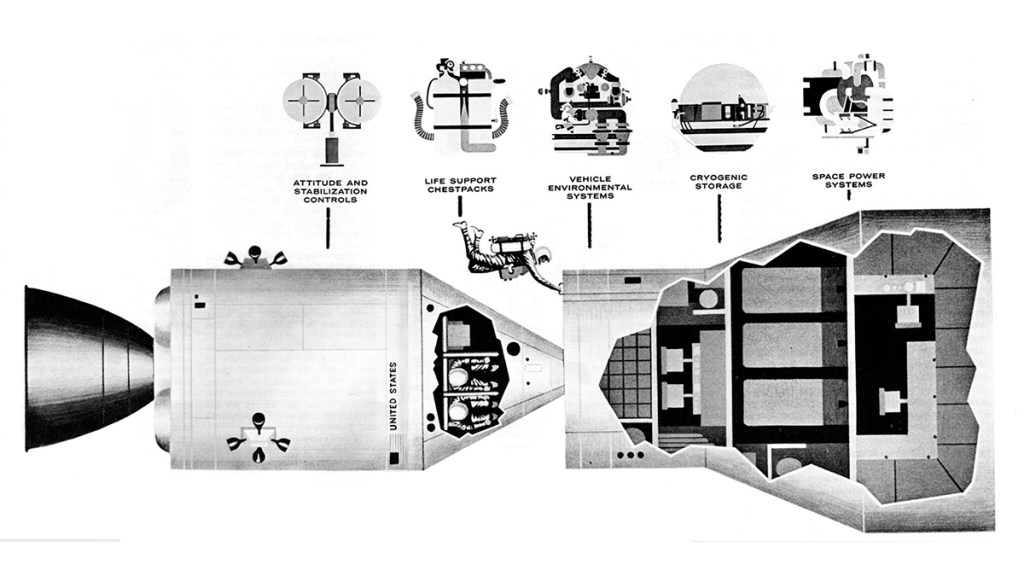
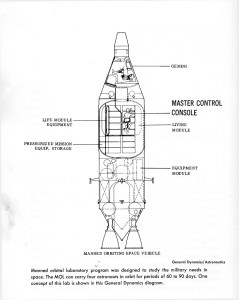
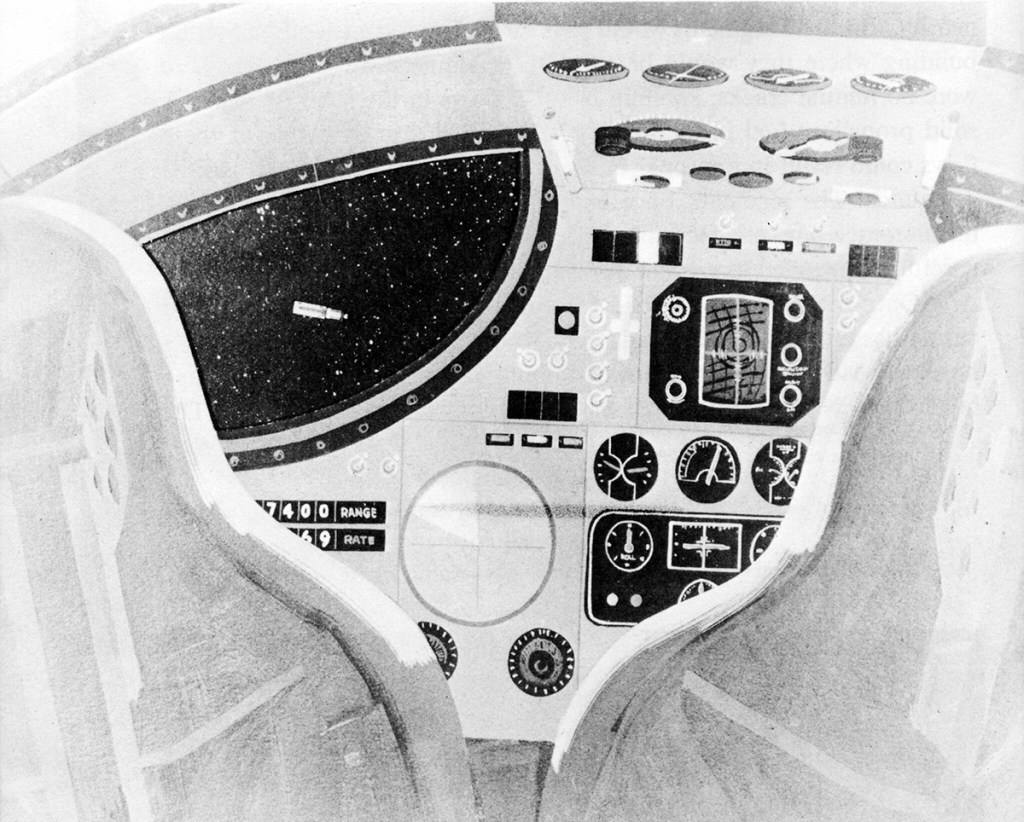
Medium-sized orbiting lab is this Manned Orbital Research Laboratory (MORL) developed for NASA’s Langley Lab by Douglas Missiles & Spacecraft Division. The lab which weighs about 35,000 pounds, could maintain 3 to 6 men in orbit for a year.
Orbiting Stations: Stopovers to Space Travel
Irwin Stambler
G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1965
Image credit: Douglas
Image source: SDASM Archives