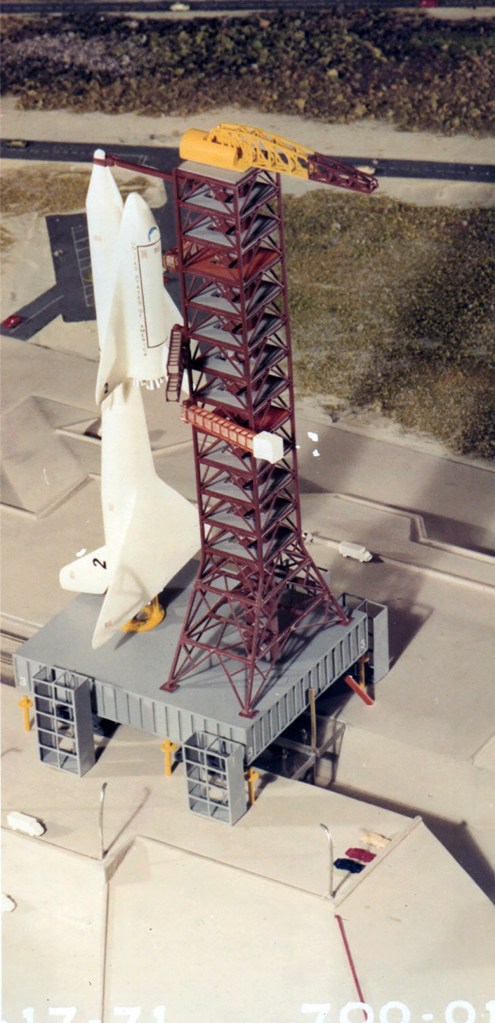
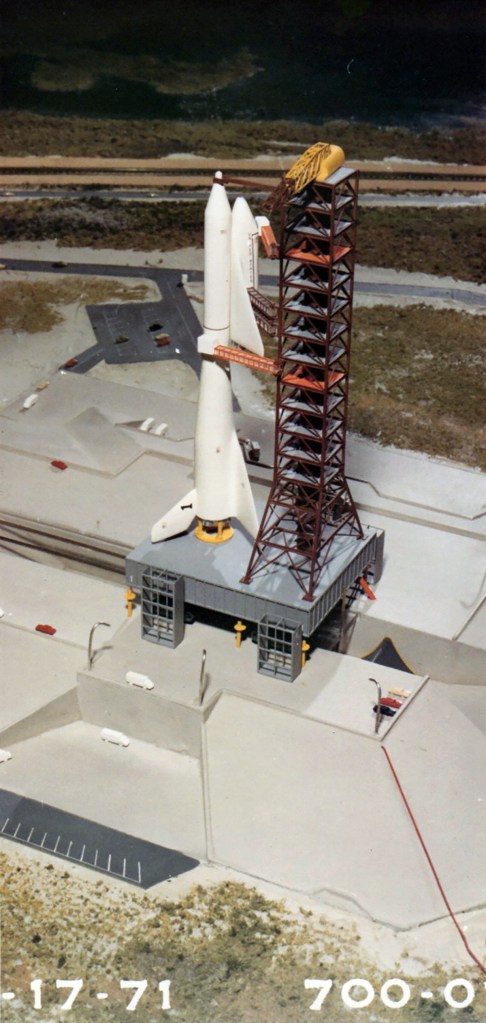
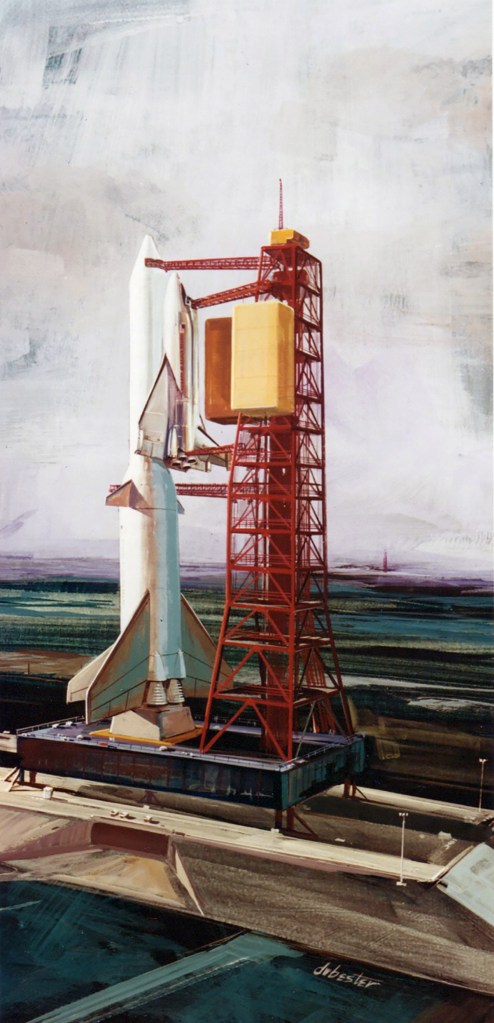
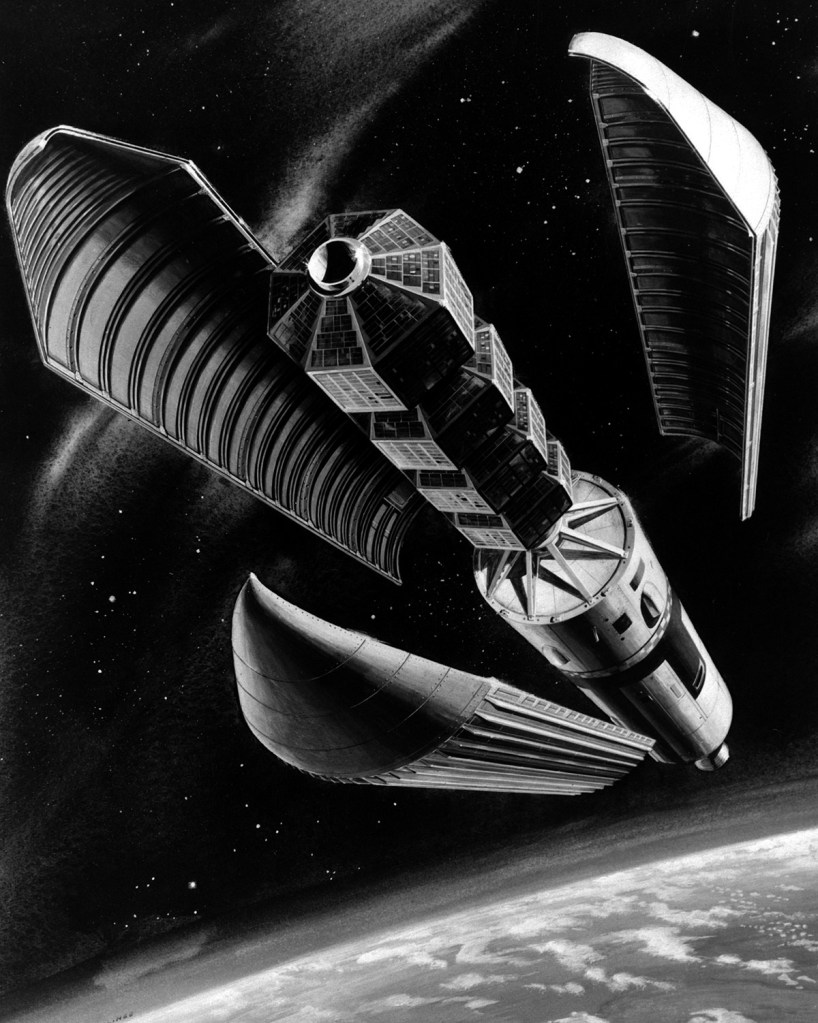
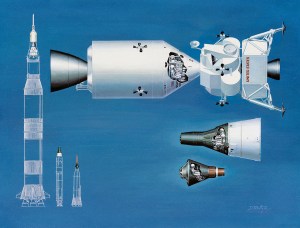
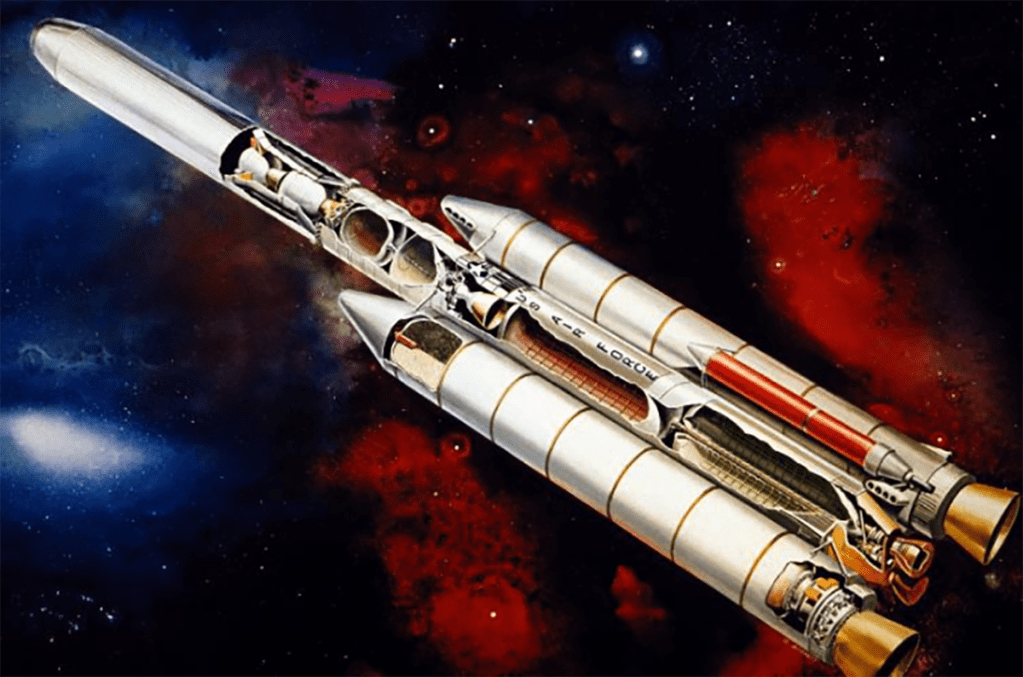
I’m pretty certain these two images are by the same hand, but which one? They’re both heavily referenced and painted in what I would describe as North American Rockwell’s house style, but the palette and brushwork bring me back to a beautiful painting Don Bester did of the Saturn Shuttle. I could be wrong, but that’s the box I’m checking for now.
Image credit: North American Rockwell
Image source: Mike Acs